Fig. 1.
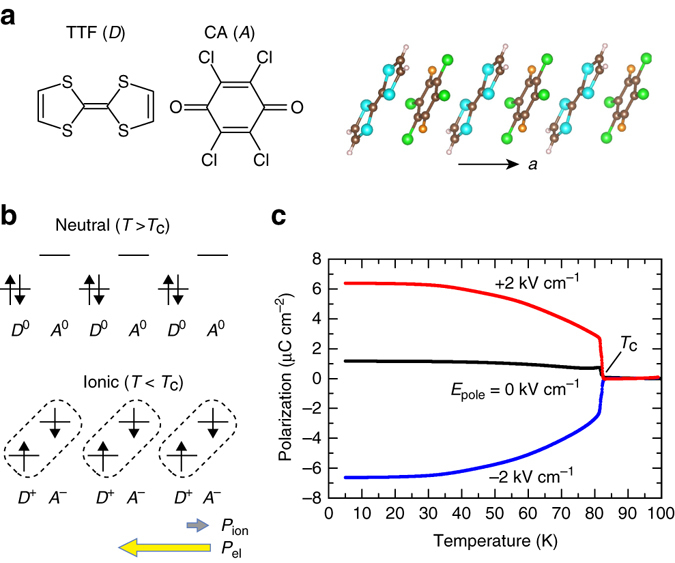
Molecular structures and neutral-to-ionic phase transition in TTF-CA. a Molecular structure of tetrathiafulvalne (TTF) and p-chloranil (CA) and the mixed stack structure of the two molecules along the a-axis. TTF is an electron donor (D) and CA is an electron acceptor (A). b Schematic electronic structures of TTF-CA in neutral and ionic phases. In the ionic phase, the dimer formation induces spontaneous polarization. The polarization has ionic and electronic contributions (P = P ion + P el). The former originates from the displacement of charged molecules, while the latter originates from the charge transfer between D–A molecules. In TTF-CA, P el is much larger than P ion and their directions are opposite. c Temperature dependence of the spontaneous polarization determined from the pyroelectric current measured after the sample was cooled under poling fields (E pole) of ±2 kV cm–1 and without the poling procedure (E pole = 0)
