Figure 3.
Mutational Analysis of the Ebox and the Hx Sites in the ZRS
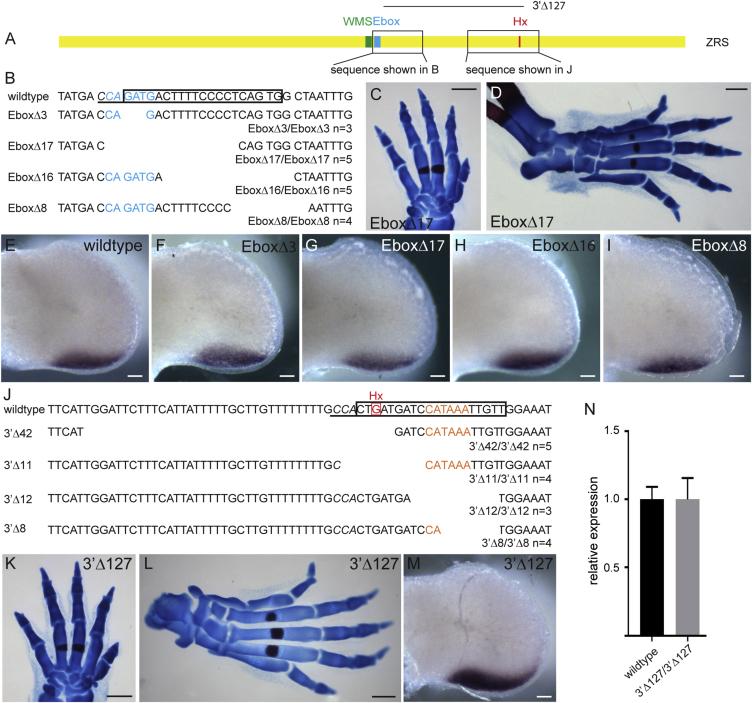
(A) The ZRS (yellow rectangle) and the relative locations of the WMS site, the Ebox, and the Hx mutation are indicated. Boxes highlight the relative positions of the sequences shown in (B) (Ebox) and (J) (Hx), respectively. Linking these two regions, the position of the 3′Δ127 deletion is also shown. The gRNA sequences are boxed in the wild-type sequences in (B) and (J) with the PAM site (italics).
(B) The EBox (highlighted in blue font) and the deleted nucleotides for each mutation. The numbers of the homozygous animals analyzed are indicated below each mutation (as n = ).
(C and D) Representative forelimb (C) and hindlimb (D) from an EboxΔ17 homozygote demonstrate no detectable deviation from the wild-type.
(E–I) Shh expression in hindlimbs on E11.5 for the wild-type (E) and EboxΔ3 (F), EboxΔ17 (G), EboxΔ16 (H), and EboxΔ8 (I) homozygotes, showing a normal pattern of expression.
(J–L) The mutant sequence affected by the 3′ deletions near Hx (J). The wild-type sequence with the position of the Hx mutation (red base and box) is indicated. The position of Hoxsite 4 is highlighted in orange. The sequences of all the deletions are shown below, and the numbers of the homozygous animals analyzed are indicated below each mutation (as n = ). The apparent unaffected forelimb (K) and hindlimb (L) of the large 3′Δ127deletion are shown.
(M and N) The levels of expression of Shh at E11.5 hindlimb buds, shown by in situ hybridization (M) and by quantification by qRT-PCR (N) in 3′Δ127 homozygous embryos.
Scale bars, 500 μm (C, D, K, and L) and 100 μm (C–I and M). Error bars indicate ± SEM.