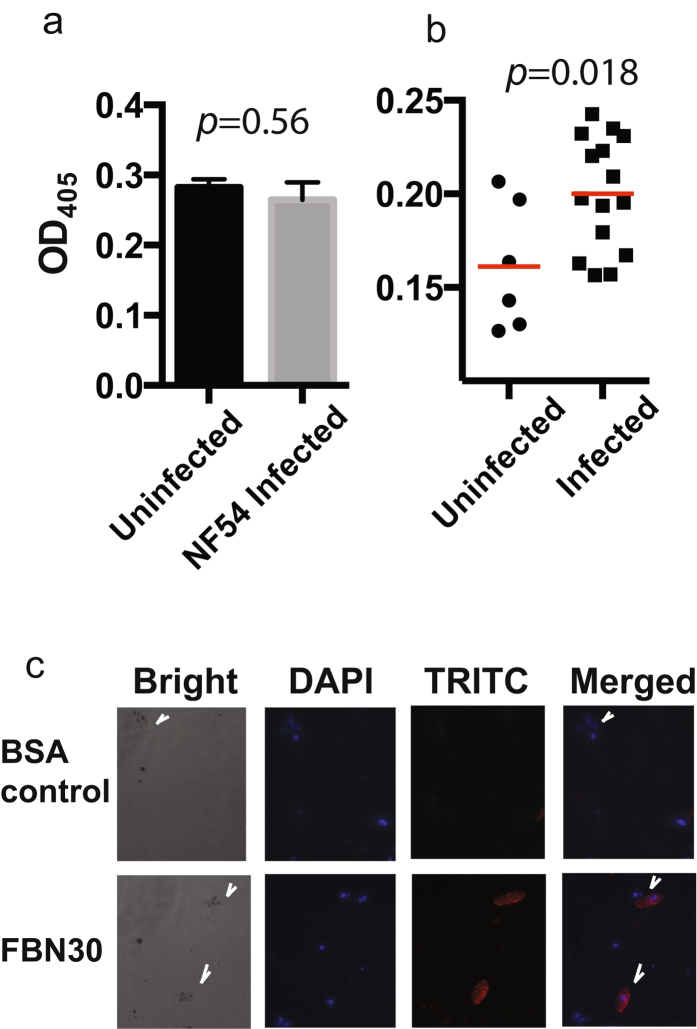
Figure 3.
FBN30 interacts with clinically circulating Plasmodium falciparum isolates. (a) FBN30 does not bind to laboratory P. falciparum strain NF54. There is no significant difference between uninfected RBC and NF54 infected RBC in ELISA assays. (b) The ELISA data show that significantly more FBN30 bound to blood lysates from the malaria infected patients (15 individuals) than that from the uninfected human subjects (6 individuals) (p = 0.018). (c) FBN30 interacts with the cultured wild type P. falciparum ookinetes determined by IFA. Images in the first row are the control group in which the anti-FBN30 was replaced with BSA. Arrows show the location of ookinetes.