Figure 1.
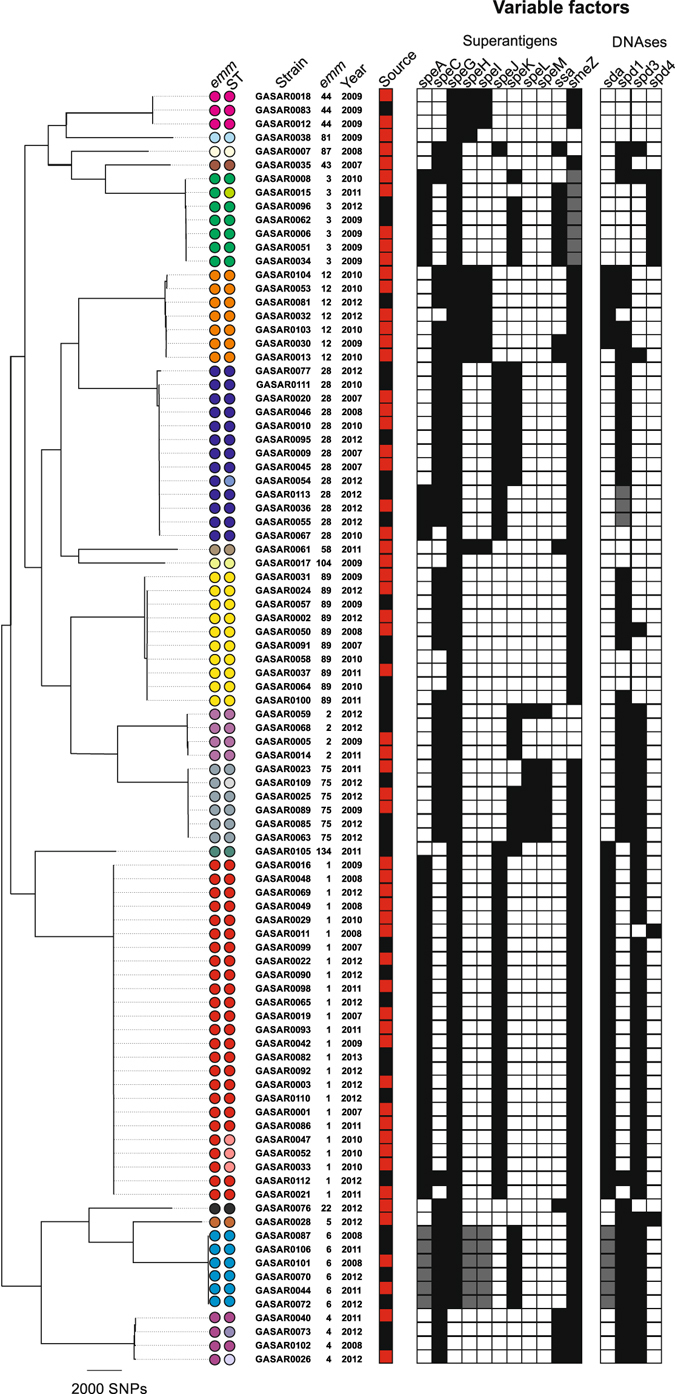
Core gene maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis of all 93 isolates. All isolates clustered by emm-type and there was a broad association of variable factor complement with the emm-type. The superantigens speA, speH and speI are highlighted in grey in emm6 strains as these are atypical variants that may not be functional. Similarly, all emm3 strains were found to carry a non-functional smeZ gene, as previously described16. The DNase spd1 in three emm28 strains is highlighted grey to indicate that it is a different variant to that found in the other emm28 strains. Coloured circles represent emm-type/ST. The majority of emm-types were associated with a single ST type (colours of emm-type identical to colour of ST). Where an additional ST was associated with an emm-type this is represent by a different colour ST circle. emm1 (n = 25); ST28 (red/red) or ST785 (red/pink), emm2 (n = 4); ST55, emm3 (n = 7); ST15 (green/green) or ST315 (green/pale green), emm4 (n = 4); ST39 (purple/purple) or ST786 (purple/pale purple) or ST38 (purple/paler purple), emm6 (n = 6); ST382, emm12 (n = 7); ST36, emm28 (n = 13); ST52 (blue/blue) or ST787 (blue/pale blue), emm44 (n = 3); ST367, emm75 (n = 6); ST150 (grey/grey) or ST788 (grey/paler grey), emm89 (n = 10); ST101. Types represented by a single isolate comprised emm5; ST99, emm22; ST46, emm43; ST3 emm58; ST176, emm81; ST624, emm87; ST62, emm104; ST789, emm134; ST790. Source; Invasive (red) or non-invasive (black) site of isolation.
