Figure 2.
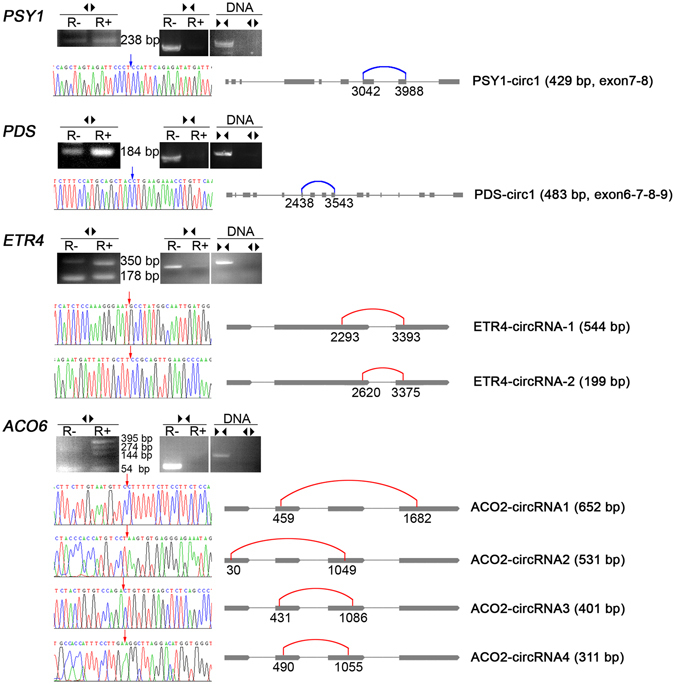
Canonical and non-canonical circRNAs validated by RNase R resistance and sequencing. RNase R resistance analysis. After DNase I treatment, total RNA from tomato fruit pericarp was digested with (R+, one hour at 37 °C) or without (R−, use water instead) RNase R. Both R+ and R− were reverse transcribed to cDNA using random primers. Divergent primers (◀▶) and convergent primers (▶◀) were used to identify circRNAs and linear RNAs respectively. Genomic DNA was also used as template to make certain that the site is not existent in genome. Sanger sequencing of divergent primers-amplified products were showed. The blue arrows and blue curves indicate canonical back-splice sites, while the red arrows and red curves indicate non-canonical back-splice sites.
