FIG 2.
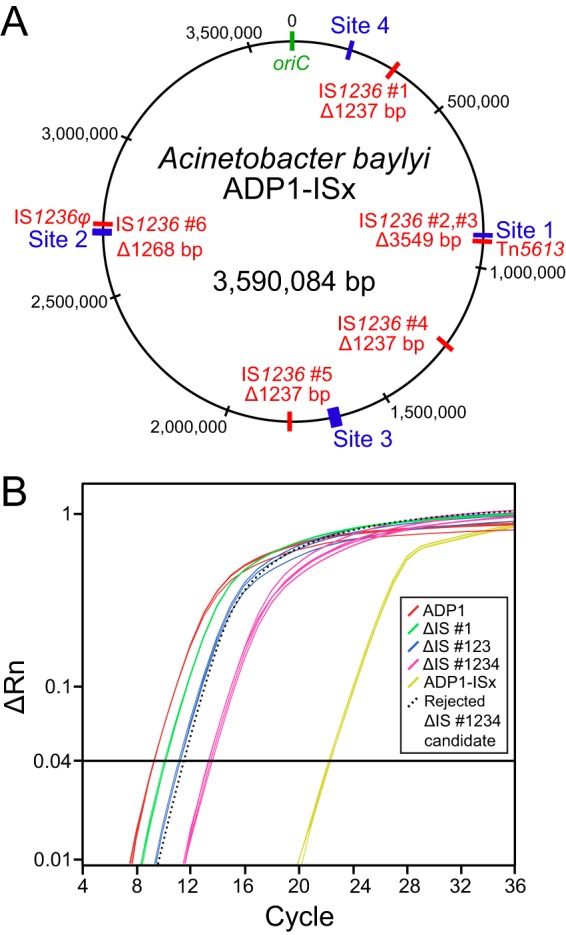
Construction of A. baylyi ADP1-ISx. (A) Five unmarked genomic deletions were made to remove all six IS1236 elements, designated by numbers 1 to 6, found in the wild-type ADP1 chromosome (shown in red) to create the ADP1-ISx strain. Sites 1 to 4 (shown in blue) were used for transformation and mutation assays. IS1236 elements number 2 and number 3 form a composite transposon (Tn5613), and element number 6 is inactive (IS1236φ). (B) Example of qPCR data used to monitor IS element deletion steps. The six IS copies per genome found in wild-type ADP1 register above a given fluorescence threshold (ΔRn value) during early PCR cycles when amplifying a 119-bp fragment located within the IS1236 transposase gene. The sequential removal of IS elements in the deletion strains progressively increases the number of cycles necessary to reach this threshold from the same input quantity of genomic DNA. One example of a rejected candidate strain that accumulated a new IS element insertion elsewhere in the genome such that its IS copy number did not decrease after the deletion of IS number 4 is shown (dotted line).
