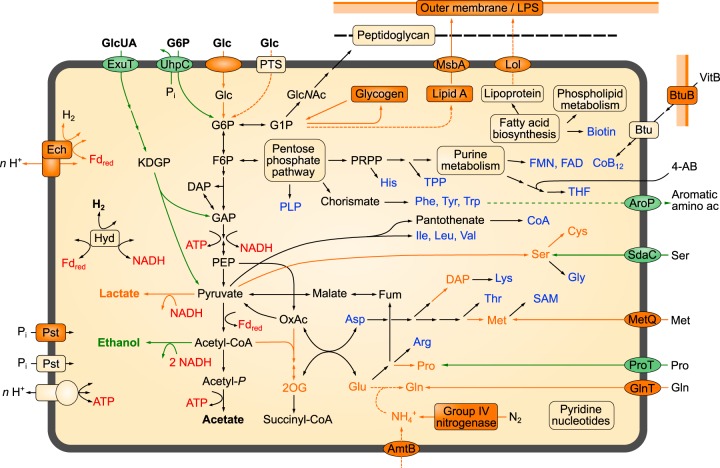
FIG 1.
Metabolic pathways in free-living En. proavitum (this study) and endosymbiotic strain Rs-D17 (12). Pathways absent or pseudogenized in the endosymbiont and their corresponding products are shown in orange; those that occur only in the endosymbiont are shown in green. Amino acids and cofactors synthesized by both strains are shown in blue; important cosubstrates in energy metabolism are shown in red. Abbreviations (gene names and IUPAC-endorsed abbreviations are not included): 4-AB, 4-amino benzoate; CoB12, coenzyme B12; DAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; Fum, fumarate; GAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate; G1P, glucose 1-phosphate; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; GlcUA, glucuronic acid; KDPG, 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate; 2OG, 2-oxoglutarate; OxAc, oxaloacetate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PLP, pyridoxal 5-phosphate; PRPP, phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate; PTS, phosphotransferase system; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; THF, tetrahydrofolate; TPP, thiamine pyrophosphate, VitB12, vitamin B12.