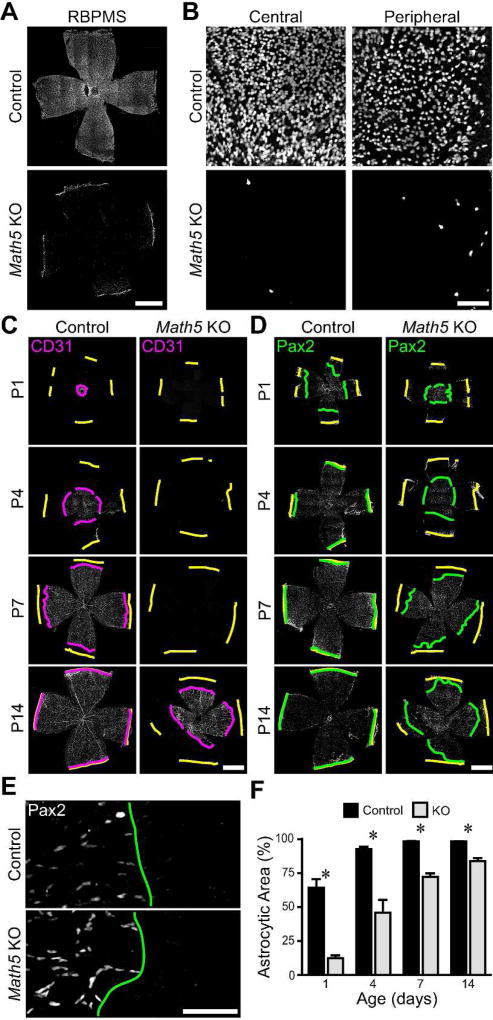
Figure 6. RGCs are required for colonization of the retina by astrocytes.
A,B) P7 Math5 knockout and control retinas were immunostained for RBPMS, a pan-RGC marker. Composite tile-scan (A) and high magnification (B) confocal images of control and knockout retinas. RBPMS-positive cells are nearly absent from knockout retinas. C,D) Composite tile-scan confocal images of flat-mounted control and Math5 null retinas immunostained for vasculature (CD31; C) or astrocytes (Pax2; D). Yellow lines: retinal edge. Magenta and green lines: CD31 and Pax2 wavefronts. Intrinsic retinal vasculature is absent until P14 (C). E) Higher magnification images from tile-scans (P1) illustrating how lines were drawn at the clear boundary between central astrocytic and peripheral astrocyte-free zones. F) Quantification of retinal area covered by astrocytes across development in controls and Math5 knockouts. Astrocytic territory is reduced and expansion delayed in knockouts. Scale bars: A,C,D) 1 mm, B,E) 100 µm.