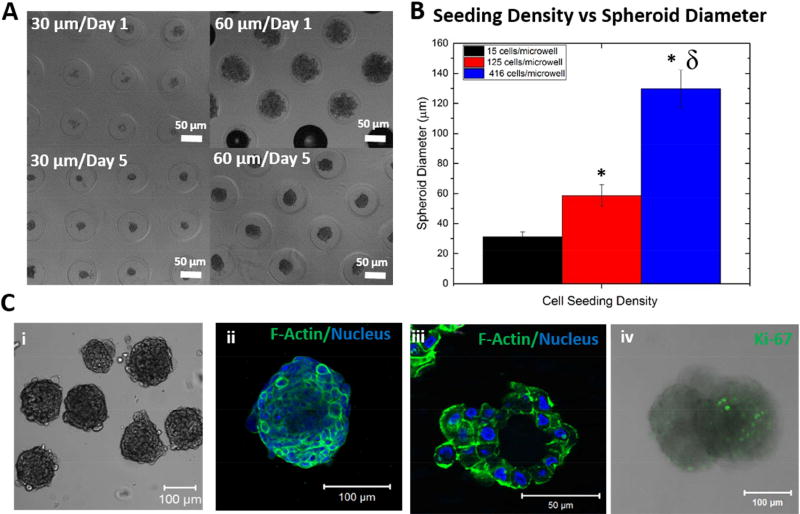
Figure 5. Construction of hS/PC spheroids.
(A-B). Spheroid diameter was adjusted by changing the initial cell seeding density (A), and the average spheroid diameter for a given cell seeding density was calculated (B, *:significantly different from spheroids with 30 µm diameter p<0.05, δ: significantly different from spheroids with 60 µm diameter p<0.05). (C) Microscopic observation of hS/PC spheroids. The bright field image shows the gross appearance of assembled structures. Confocal images were acquired on the entire spheroid as a Z-stack (ii) and on a cryosectioned slice to show the central lumen (iii). F-actin and nuclei were stained green and blue, respectively. The combined fluorescence and bright field image (iv) showed the presence of proliferative cells, stained green for Ki67.