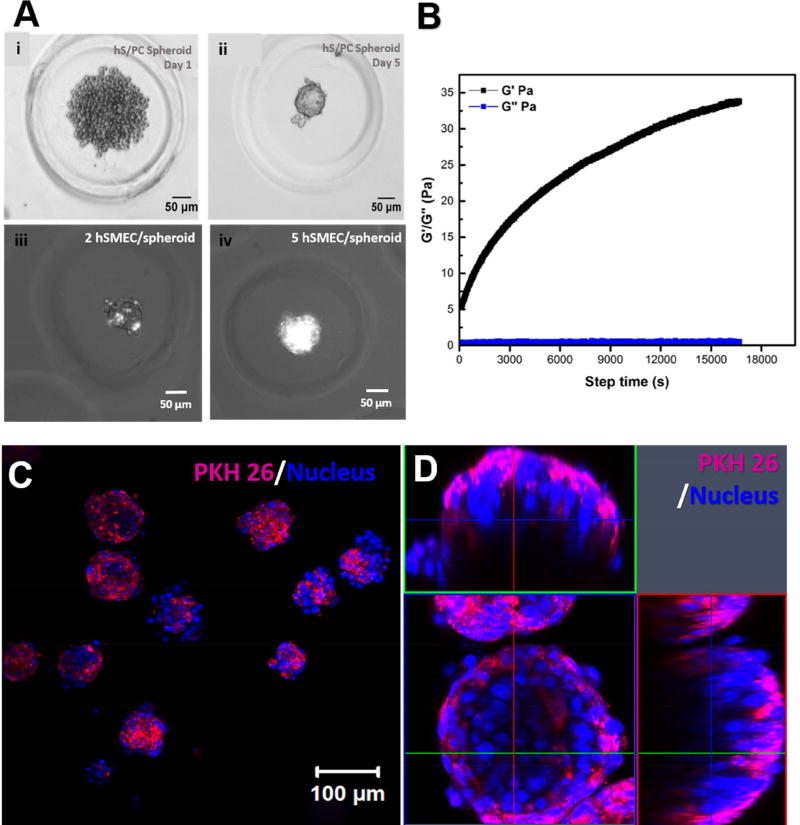
Figure 6. Morphological characterization of hS/PC-hSMEC co-assemblies.
(A) Evolution of the microtissue from the initial loose hS/PC aggregates (i), to compact spheroids (ii), and the optimization of hSMEC/spheroid ratio to achieve a complete coverage of hS/PC spheroids by hSMECs (iii, iv). (B). Rheological characterization of HA/PEG gels used to encapsulate the assembled microtissues. A representative time-sweep result is shown. (C, D) Confocal images of 3D encapsulated salivary gland microtissues at low (C) and high magnifications (D). Expanded horizontal and vertical views shown in D revealed the spatial arrangement of the two cell types in the microtissue. hSMECs (labeled magenta with PKH26) localized on the outer surface of the structure. Cell nuclei were stained blue.