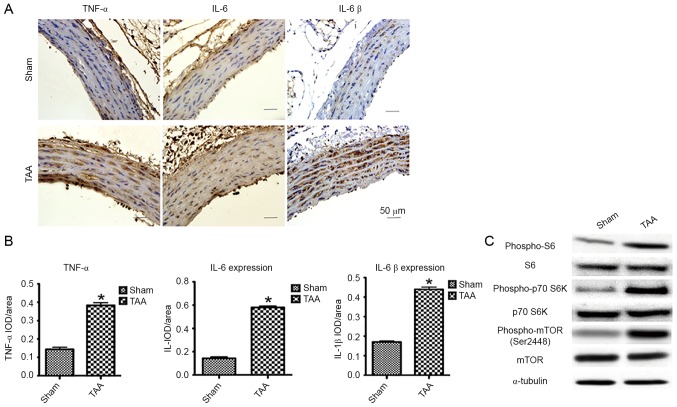
Figure 1.
The effect of proinflammatory cytokines and mTOR signaling 2 days following TAA induction. (A) Representative pictures of the immunohistochemical study in aortic segments 2 days post-TAA induction. The slides were stained with TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β. The anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase/diaminobenzidine detection system was used to visualize the expression (brown staining). Scale bar, 50 µm. Sham: NaCl-treated group (n=6). TAA: CaCl2-treated group (n=6). (B) Quantitation of the protein content of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β was performed by computerized planimetry in the aortic adventitia and aortic media in immunohistochemically stained slides. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of mean, *P<0.05 vs. the Sham group. (C) Representative western blots demonstrated the upregulation of phosphorylation of proteins involved in the mTOR signaling pathway in the CaCl2-treated segment of aorta as early as 2 days, including phospho-mTOR, phospho-p70 S6K and phospho-S6. TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL, interleukin; TAA, thoracic aortic aneurysm; IOD, integral optical density.