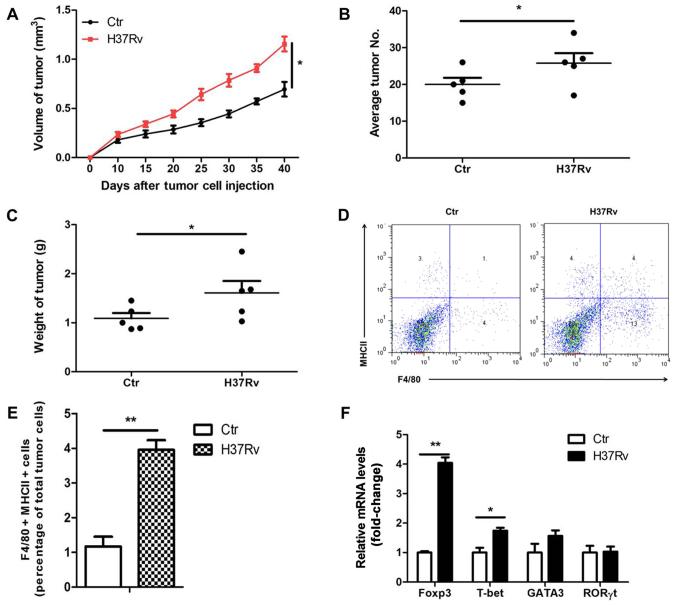
Figure 1.
H37Rv infection promotes tumor growth in a mouse model. (A) Tumor growth was measured over time (n=10). (B) Number of lung tumor nodules in mice 40 days after intravenous tumor inoculation (n=10). (C) Tumor mass 40 days after tumor cell inoculation (n=10). (D and E) F4/80+MHCII+ tumor-associated macrophages were detected by flow cytometry. (F) CD4+ T cell changes in the draining lymph nodes after H37Rv infection. All experiments were representative of three similar results. Statistical differences between groups are indicated by the P-values. *P<0.05; **P<0.01.