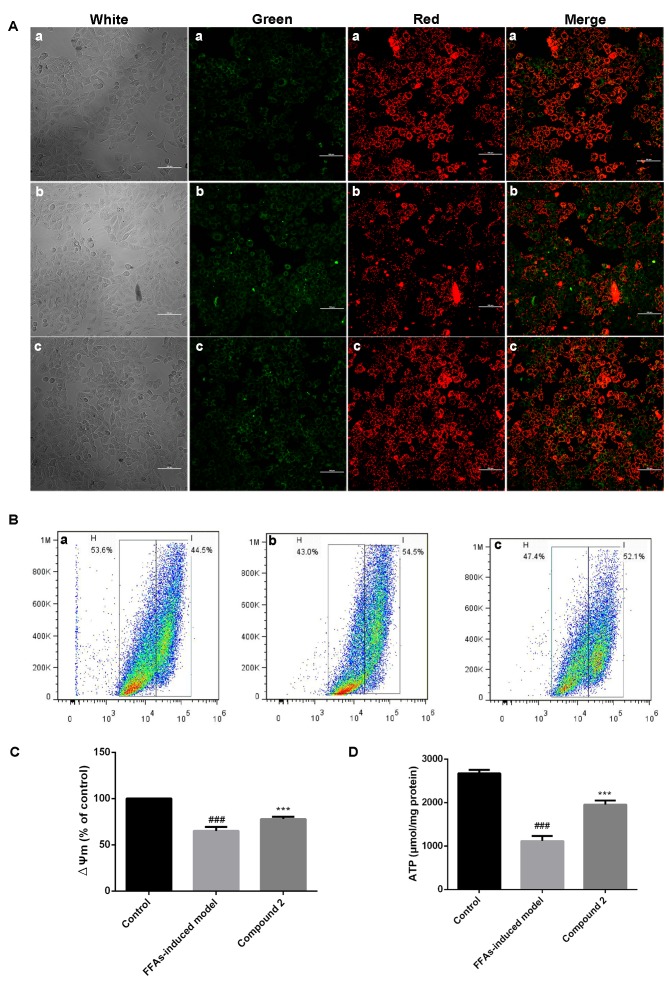
Figure 5.
Compound 2 prevented the ∆Ψm collapse and maintained cellular ATP levels in FFA-treated HepG2 cells. Human HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells were treated with 1 mmol/l FFAs alone or together with compound 2 (25 µmol/l) for 24 h. (A) JC-1 staining was used to assess ∆Ψm. Red fluorescence indicates high ∆Ψm, whereas green fluorescence indicates low ∆Ψm. (a) Control cells; (b) FFA-treated cells; (c) FFA- and compound 2-treated cells. Photomicrographs were captured under ×400 magnification. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of ∆Ψm, assessed using JC-1 fluorescence. (a) Control cells; (b) FFA-treated cells; (c) FFA- and compound 2-treated cells. (C) Relative ∆Ψm levels were quantified in control, FFA- and FFA- and compound 2-treated cells. (D) Intracellular ATP levels were assessed in control, FFA- and FFA- and compound 2-treated cells. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. ###P<0.001 vs. control cells; ***P<0.001 vs. FFA-treated cells. Compound 2, eriodictyol 7-O-β-D glucopyranoside; ∆Ψm, mitochondrial membrane potential; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; FFA, free fatty acid.