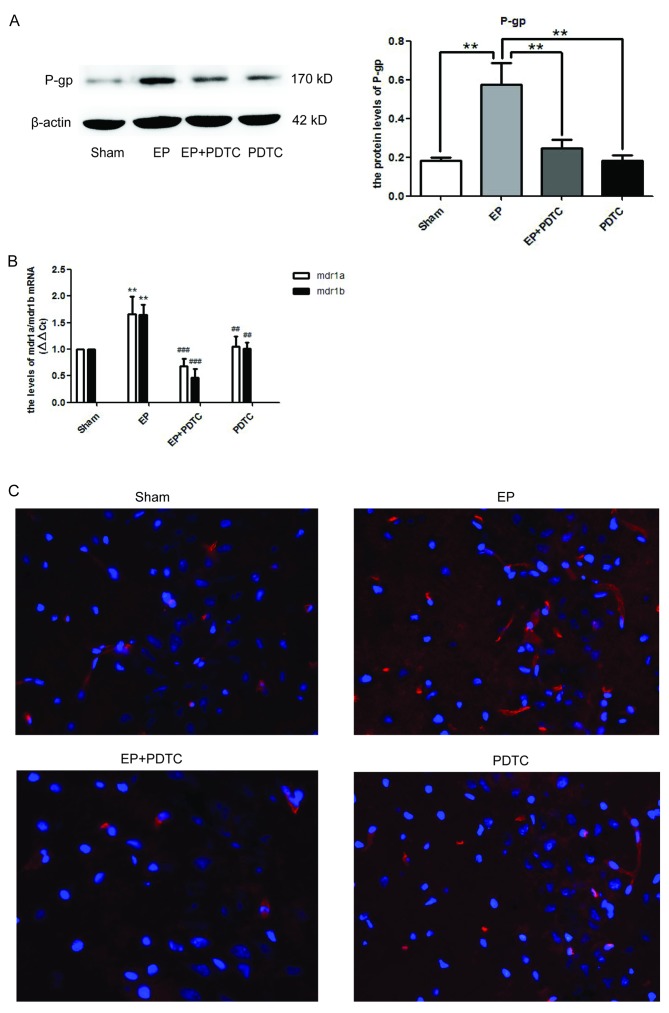
Figure 4.
Inhibition of NF-κB by PDTC reduces the expression levels of P-gp in epileptic rat brains. (A) P-gp expression levels in each group were detected at 72 h following termination of status epilepticus by western blotting. Densitometry analysis was performed and data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. PDTC significantly reduced the expression levels of P-gp in the EP + PDTC compared with the EP and Sham groups (**P<0.01). However, there was no statistical difference in expression between the EP + PDCT and PDTC groups. (B) mRNA expression levels of MDR1A/B were significantly enhanced in the EP group compared with the sham group, and were significantly reduced in the EP + PDTC compared with the PDTC group. (P<0.01 vs. sham; ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.0001 vs. EP). (C) Expression and localization of P-gp in hippocampal region CA3 of rat brains. Blue=nuclei and red=P-gp. Images were captured using ×400 magnification. Compared with the EP group, P-gp was reduced in the EP + PDTC group and was primarily localized to blood vessels. NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PDTC, pyrrolidinedithiocarbamic acid; P-gp, P-glycoprotein; EP, pilocarpine-induced epilepsy group.