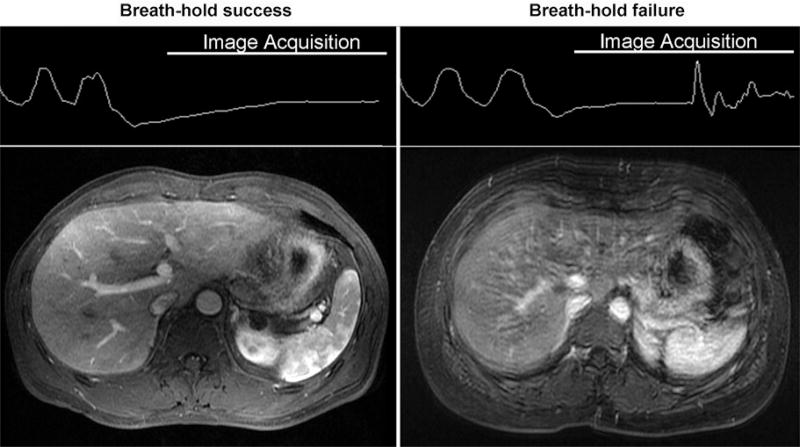
Figure 2.
Respiratory bellows were used to monitor the success of breath holding. Breath-hold success was defined as a straight or slowly varying trace during image acquisition. Breath-holding failure was recognized as the occurrence of sudden oscillations in bellows tracing in this figure. The example images were obtained in a 50-year-old man (success) and a 67-year-old man (failure).