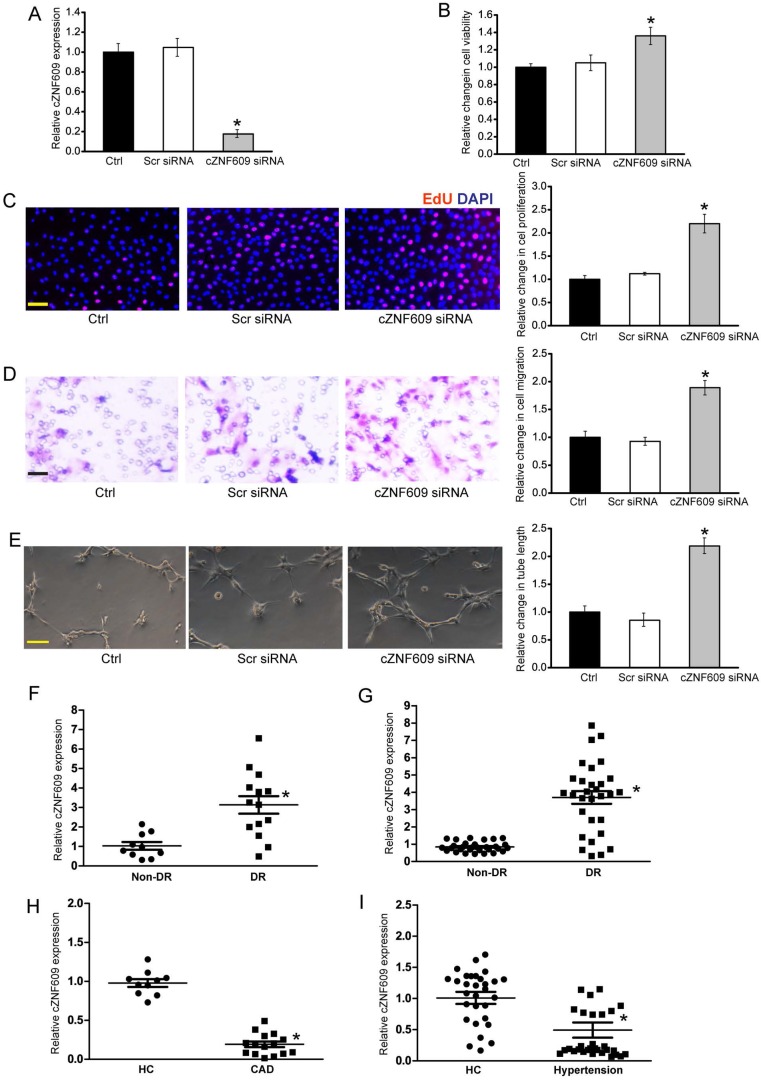
Figure 7.
Clinical relevance of cZNF609 dysregulation in vascular disease (A) Human retinal endothelial cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA (Scr), cZNF609 siRNA, or left untreated (Ctrl) for 48 h. qRT-PCRs were conducted to detect cZNF609 expression (n=4, *P<0.05). (B) Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Result was shown as relative change compared with Ctrl group (n=4, *P<0.05). (C) Cell proliferation was detected by EdU detection kit (n=4, *P<0.05). Scale bar, 200 μm. (D) Transwell assay and quantification analysis was used to detect cell migration (n=4, *P<0.05). Scale bar, 20 μm. (E) Human retinal endothelial cells were seeded on the matrigel matrix. Tube-like structures were observed 24 h after cell seeding. Average length of tube formation for each field was statistically analyzed (n=4, *P<0.05). Scale bar, 100 μm. (F) qRT-PCRs were performed to detect cZNF609 expression in the fibrovascular membranes of diabetic patients (n=15) and idiopathic epiretinal membranes of non-diabetic patients (n=10) (*P<0.05 versus non-diabetic controls). (G) qRT-PCRs were conducted to detect cZNF609 expression in EDTA-plasma obtained from diabetic patients (n=30) and non-diabetic controls (n=30) (*P<0.05 versus non-diabetic controls). (H) cZNF609 expression in EDTA-plasma obtained from the patients with CAD (n=15) and healthy volunteers (HC; n=10) was determined by qRT-PCRs. (I) cZNF609 expression in EDTA-plasma obtained from patients with hypertension (n=30) and healthy volunteers (HC; n=30) was determined by qRT-PCRs.