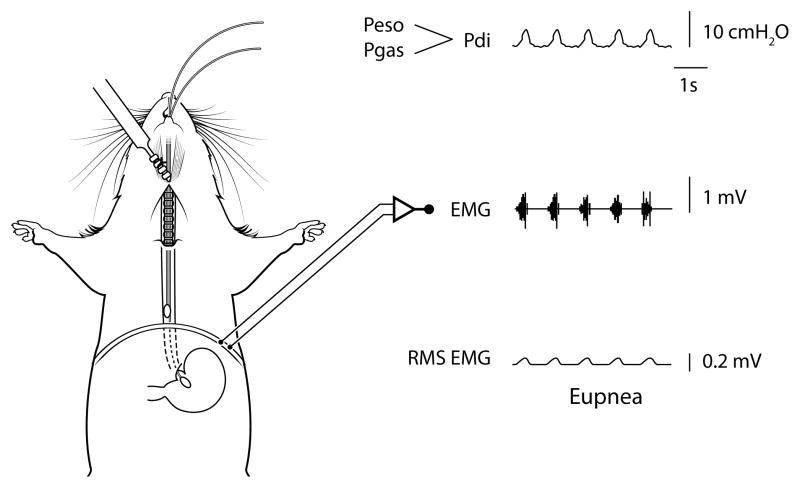
Figure 5.
Anatomical schematic showing placement of the solid-state pressure catheters for measurement of gastric (Pgas) and thoracic esophageal (Peso) pressures in mice - note the pair of catheters are advanced into the stomach (Pgas) and esophagus in the thoracic cavity (Peso) through the mouth. The difference between Pgas and Peso is used to determine transdiaphragmatic pressure (Pdi; see raw tracing). The Pdi amplitude is significantly correlated to peak root mean squared (RMS) of diaphragm muscle electromyography (EMG) activity (2, 3). Raw tracings are provided for Pdi, diaphragm EMG, and RMS EMG.