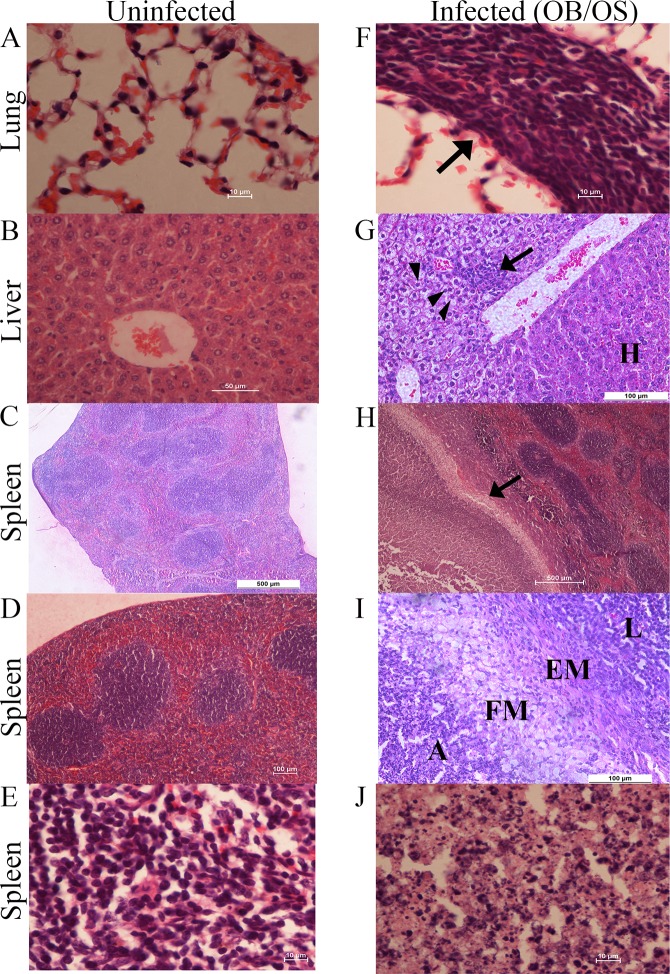
Fig 2. Histopathological changes of lungs, livers, and spleens of mice with persistent B. pseudomallei infections.
(A) Lung (B) liver and (C-E) spleen of uninfected mice show normal histopathology. (F) Non-necrotic solid lung lesions characterized by a discrete focus consisting of primarily mononuclear cells (arrow). (G) Hepatic lesion with predominantly mononuclear cells (arrow). Cytoplasmic vacuolation of hepatocytes were observed in the area surrounding the lesion, which is characterized by swelling hepatocytes and clearing cytoplasm (arrow heads) Normal hepatocyte-H. (H) Splenomegaly with large encapsulated abscess cavity (arrow). (I) The encapsulated abscess-A was surrounded by foamy macrophages-FM, epithelioid macrophages-EM, and lymphocytes-L. (J) Magnification of the splenic encapsulated abscess, which contains neutrophils, mononuclear cells, bacteria, and necrotic cellular debris. Sections were stained with H & E. Scale bars: 10 μm (A, E, F, J), 50 μm (B & G), 100 μm (D & I) and 500 μm (C & H). Data are representative of one experiment (n = 4 per group).