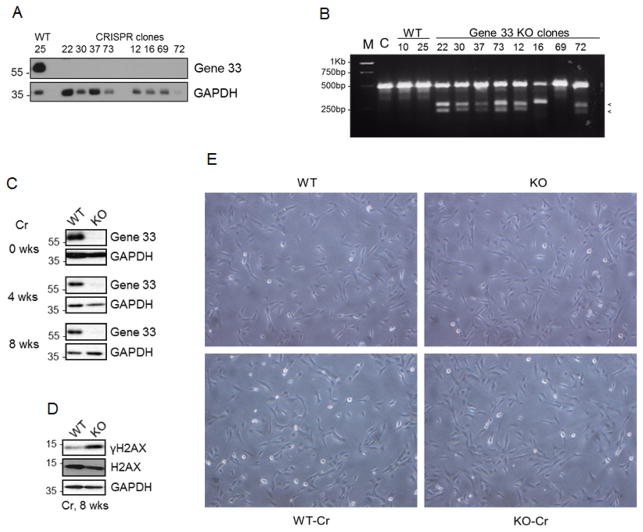
FIGURE 1. CRISPR/cas9-mediated Gene 33 deletion and chronic sublethal Cr(VI) exposure did not cause visible morphological changes of BEAS-2B cells.
A. CRISPR/cas9-mediated Gene 33 deletion was carried out in BEAS-2B cells as described in Materials and Methods. Clones of control (WT) and Gene 33 deletion (KO) cells were isolated and expanded. Total cellular proteins of these cells were collected and subjected to Western blot (WB) to detect Gene 33. GAPDH was used a loading control. B. The T7E1 assay was performed using primers described in Materials and Methods on WT and KO cell clones. The appearance of two small DNA fragments indicates indel formation. M: DNA marker, C: the parental BEAS-2B cells. C. WB showing expression of Gene 33 at different time points after Cr(VI) treatment at 0.5 μM in WT and KO cells. D. WB showing the levels of γH2AX in WT and KO cells after 8 week treatment with Cr(VI) at 0.5 μM. E. Morphology of WT and KO cells with or without Cr(VI) treatment at 0.5 μM for 8 weeks. Pictures were taken at 60X.