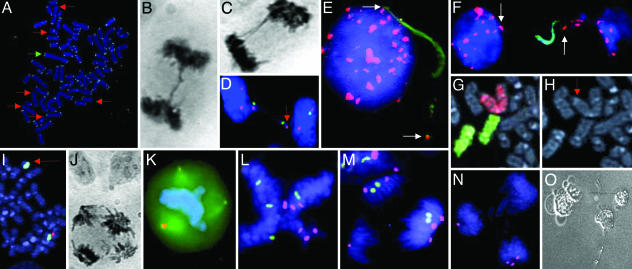
Fig. 1.
Cytogenetic analyses and single-cell cloning. (A) TTAGGG-negative ends (red arrows) and a dicentric chromosome (green arrow) in SW480. (B and C) Anaphase bridges in DLD1 (B) and SW480 (C). (D) Loss of chromosomes X (arrow; centromere in green) and 18 (centromere in violet) through bridge formation in SW480. (E and F) Fragmented DNA (green) flanked by alphoid repeats (arrows; red) in SW480. (G and H) A dicentric chromosome 7 derivative (red chromosome paint in G; red arrow in H) and two normal chromosomes 12 (green chromosome paint in G) in HT29. (I) A ring chromosome positive with the 7q31 probe (green) but not with the chromosome 7 alphoid probe (red) in the HCT116 subclone M7. (J and K) A tetrapolar anaphase cell in hematoxylin-eosin staining (J) and a tripolar metaphase cell with three centrosomes (K)(γ-tubulin in orange) in SW480. (L–N) FISH analyses with centromeric probes in SW480 showing a tetrapolar metaphase cell with four copies of the X chromosome (green) and six copies of chromosome 18 (violet) (L), a tripolar anaphase cell with 2 + 2 + 0 segregation of chromosome X and 3 + 2 + 1 segregation of chromosome 18 (M), and a tripolar anaphase cell with 3 + 1 + 0 segregation of chromosome 18 (N). (O) Degenerating daughter cells of an isolated tetrapolar mitotic cell from the same cell line. (Magnifications: ×1,000, A, E, and I; ×100, B–D, F, and J–N; ×2,000, G and H; and ×40, O.)