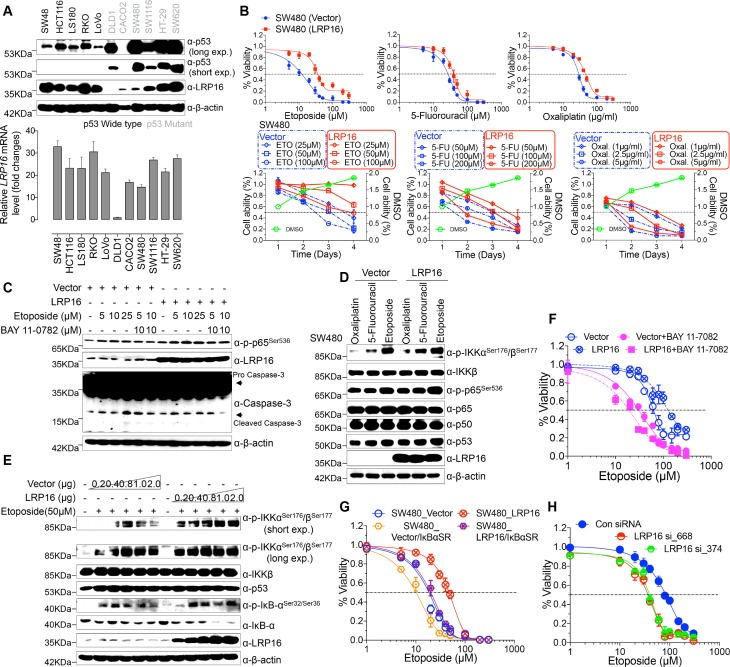
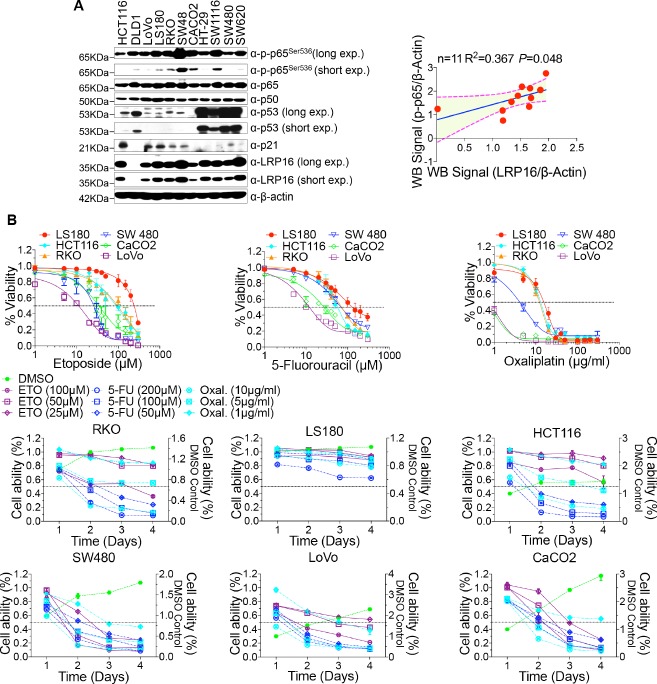
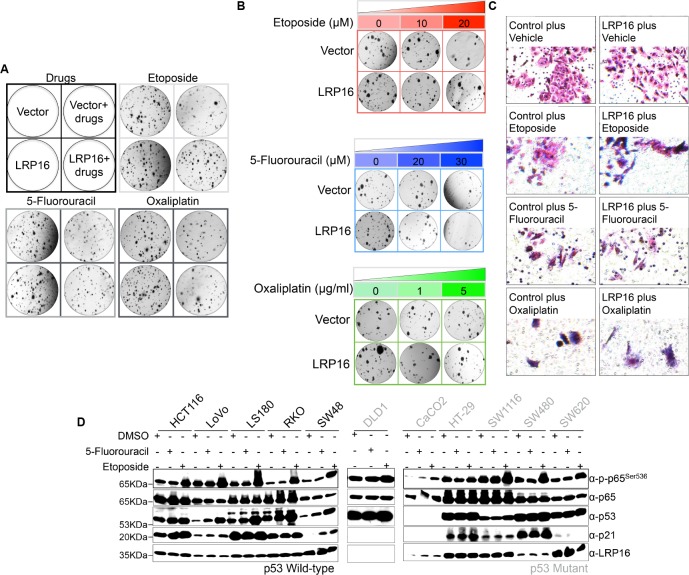
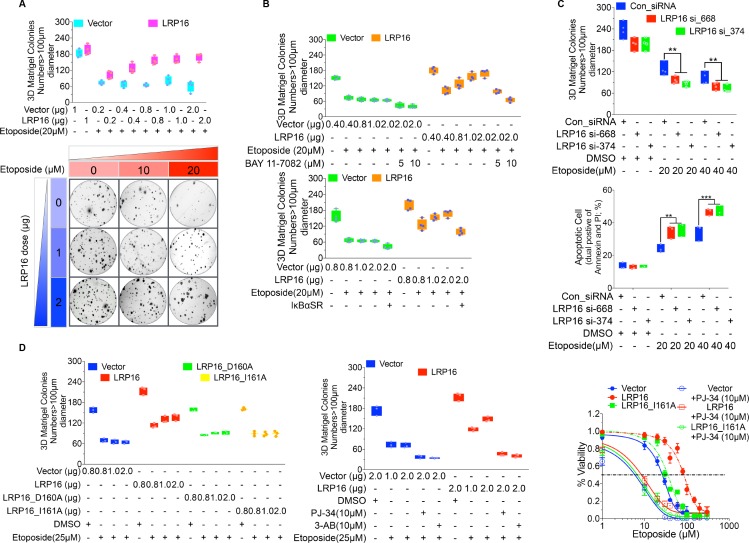
Figure 2. LRP16 mediates acquired resistance to etoposide in CRCs.
(A) Expression levels of LRP16 were analyzed in 11 CRC cell lines with Western blotting and RT–qPCR. (B) Cell growth assay. SW480 cells were transfected with the control vector or an LRP16-expressing plasmid for 48 hr, and then treated with etoposide, 5-fluorouracil, or oxaliplatin for a further 72 hr. Cell viability was determined with a CCK-8 assay. (C) SW480 cells transfected with an LRP16-expressing plasmid or the control vector were treated for 36 hr with the indicated concentrations of etoposide and/or BAY 11–7082. Cell lysates were separated with SDS-PAGE and analyzed with Western blotting using the indicated antibody. β-Actin was used as the loading control. (D) SW480 cells transfected with an LRP16-expressing plasmid or the control vector were treated with etoposide (50 μM), 5-fluorouracil (100 μM), or oxaliplatin (2 μg/ml) for 3 hr, and the cell lysates were analyzed with Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (E) SW480 cells transfected with increasing doses of an LRP16-expressing plasmid or the control vector were treated with etoposide (50 μM), and then immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (F) SW480 cells transfected with an LRP16-expressing plasmid or the control vector were pretreated with or without BAY 11–7082 and then treated with etoposide for indicated concentrations, and subjected to a cell viability analysis. (G) SW480 cells transfected with the indicated plasmids and treated with etoposide for indicated concentrations, and subjected to a cell viability analysis. (H) SW620 cells were transfected with control or LRP16-directed shRNAs, and the resulting stable cells were treated with etoposide and subjected to a cell viability analysis. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.