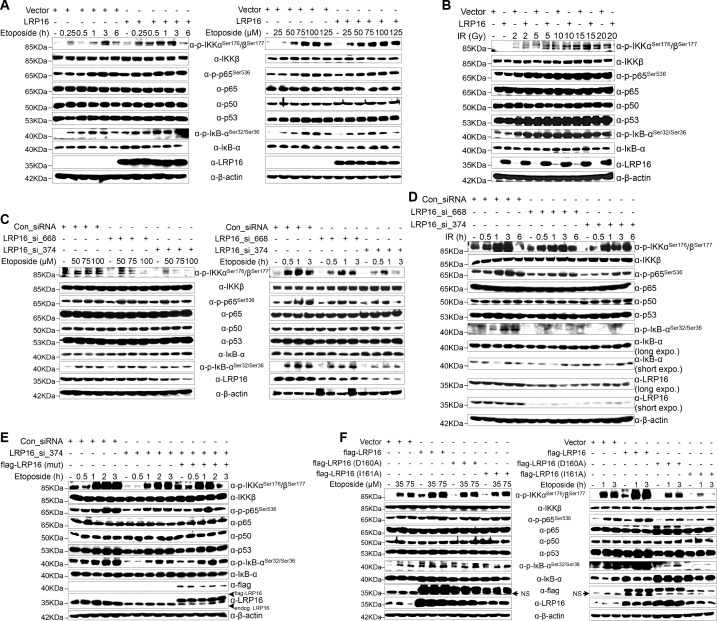
Figure 3. LRP16 is required for genotoxicity-induced NF-κB activation.
(A) Whole cell lysates from cells transfected with an LRP16-expressing plasmid or the control vector were treated with the indicated concentrations of etoposide for 2 hr or with 50 μM etoposide for the indicated periods, and then immunoblotted with the indicated antibody. β-Actin was used as the loading control. (B) SW480 cells transfected with an LRP16-expressing plasmid or the control vector were treated with IR for the indicated dose. The cell lysates were then separated with SDS-PAGE and analyzed with Western blotting using the indicated antibody. (C) Whole-cell lysates from SW620 cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs and treated with the indicated concentrations of etoposide for 2 hr or with 50 μM etoposide for the indicated periods were immunoblotted with the indicated antibody. β-Actin was used as the loading control. (D) SW620 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and exposed to IR for the indicated periods. Their lysates were separated with SDS-PAGE and analyzed with Western blotting using the indicated antibody. (E) SW620 cells were cotransfected with the indicated siRNAs and/or the LRP16-expressing vector that contained silent mutations in the sequences that targeted by the LRP16 siRNAs, and were then treated with 50 μM etoposide for the indicated periods. The cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated antibody. (F) Whole cell lysates of cells transfected with the control vector or vectors expressing LRP16 or the LRP16 mutants (LRP16_D160A, LRP16_I161A) and treated with the indicated concentrations of etoposide for 2 hr or with 50 μM etoposide for the indicated periods were immunoblotted with the indicated antibody. β-Actin was used as the loading control. One representative experiment of three was shown.
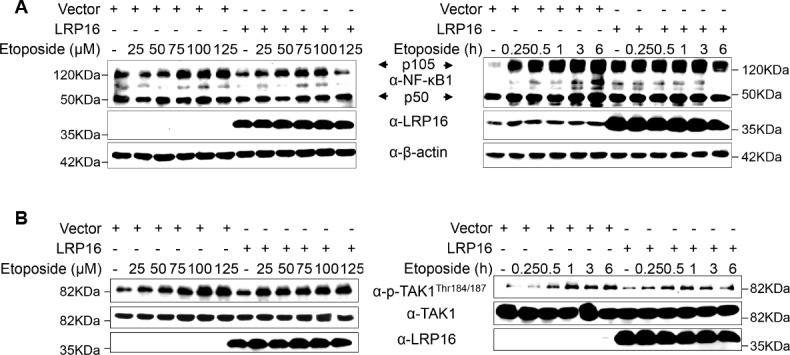
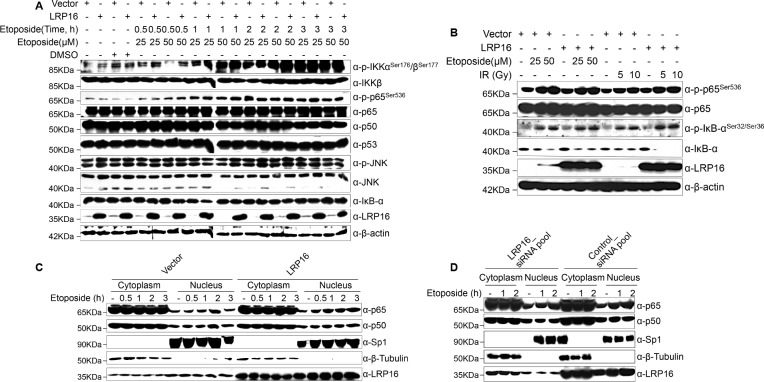
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. LRP16 executes an essential function in the nuclear-initiated NF-κB signaling in response to DNA damage.
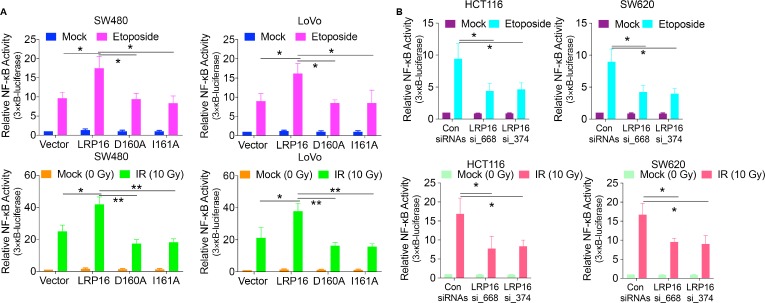
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. LRP16 is required for NF-κB transactivation in response to genotoxic stress.