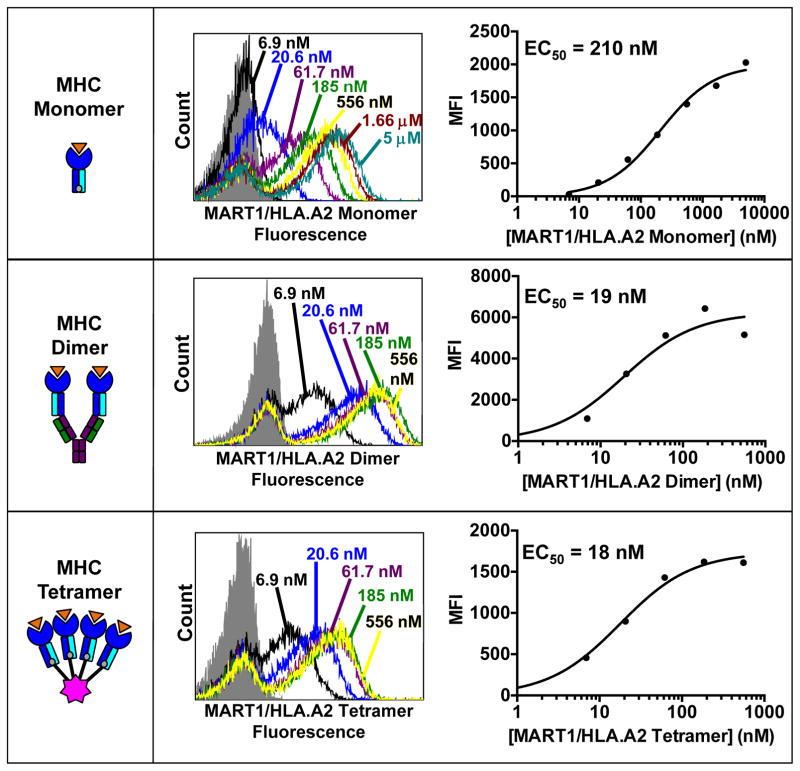
Fig. 4. Peptide-MHC ligands for the selection and analysis of T cell receptors.
(Left panels) Schematics of pepMHC monomers, dimers, and tetramers are shown, where orange represents peptide, blue represents MHC heavy chain, and cyan represents MHC light chain. MHC monomers (top) are biotinylated and are used with a PE-conjugated SA secondary reagent to stain yeast-displayed TCRs. MHC dimers (middle) are fused to an mouse immunoglobulin and are used with a fluorophore-conjugated Goat anti-Mouse IgG secondary antibody to stain yeast-displayed TCRs. MHC tetramers (bottom) are directly bound to a PE-conjugated streptavidin molecule and can be used to stain yeast-displayed TCRs directly. (Center panels) Flow cytometry histograms showing the yeast staining profiles of the T1-S18.45 scTv, which binds to MART-1/HLA-A2, with the three pepMHC reagents at the indicated concentrations. The gray shaded curve represents yeast stained with secondary reagent only. (Right panels) Plots of the mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) obtained from the flow histograms at each concentration. EC50 values obtained from nonlinear regression analysis of the plots are shown in the inset.