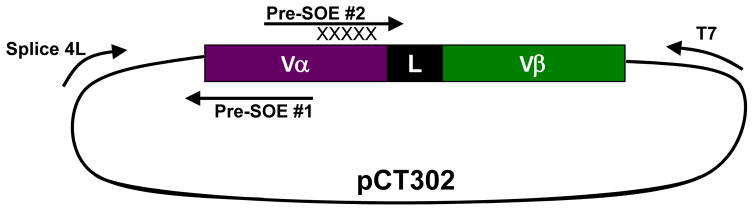
Fig. 6. A schematic of splicing by overlap extension (SOE) PCR for creating site-directed CDR libraries.
In order to generate site-directed libraries in CDR loops, the N-terminal portion of the gene and C-terminal portion of the gene between standard Splice4L and T7 primers are amplified separately to include a 25–35 nucleotide overlap just prior to the degenerate regions. Pre-SOE #1 is generated via PCR of the Splice4L primer and a reverse primer designed to contain the 25–35 nucleotide overlap and an additional 25–35 nucleotides upstream. Pre-SOE #2 is generated via PCR of a forward primer designed to contain the 25–35 nucleotide overlap followed by the degenerate (NNS or NNK) codons and an addition 25–35 nucleotides downstream. Following separate amplification of PreSOEs #1 and #2, a SOE reaction containing both Pre-SOEs and Splice4L and T7 primers is used to amplify the entire gene product from Splice4L to T7. The resultant PCR product can be used directly to generate libraries via homologous recombination in yeast.