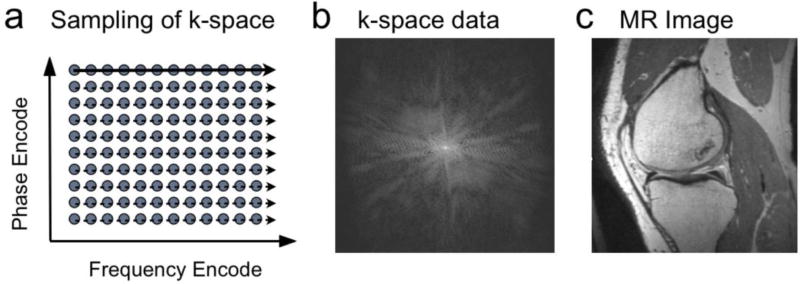
Figure 3.
In conventional MRI, samples of data are acquired in “k-space.” (a). On each excitation samples are taken along a line of locations in the frequency-encode direction over time (solid, dashed arrows). On different excitations, the location of these samples in the phase-encode direction is changed. The sampled data in k-space (b) consists of signal strengths at each location, and can be Fourier transformed to obtain the corresponding image (c).