Figure 4. Structural characterization of solubilized DsbB by biological SAXS.
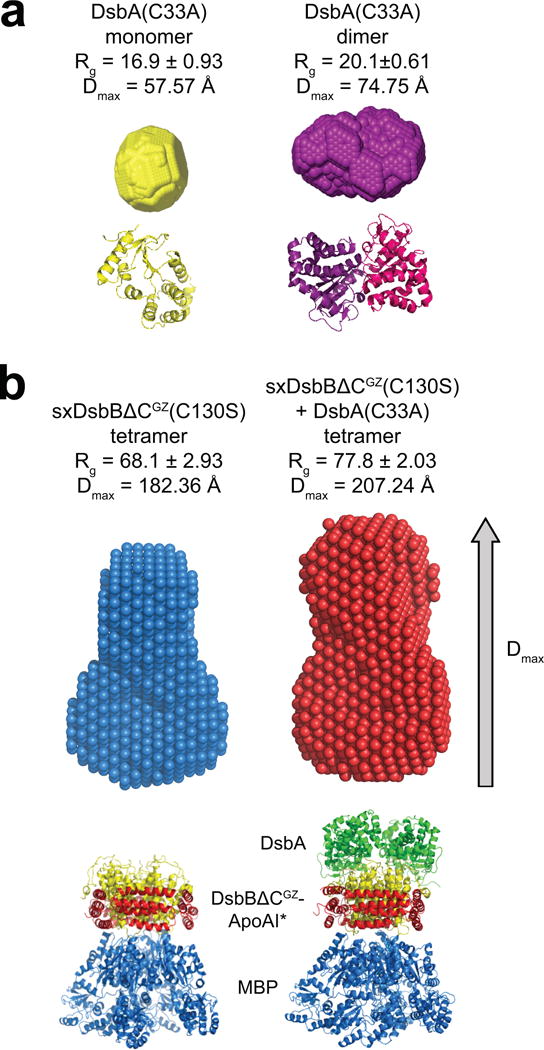
Reconstructed particle envelopes calculated ab initio from the SAXS data for cDsbA(C33A) as a monomer (yellow) or dimer (purple) (a) and tetrameric SxDsbBΔCGZ(C130S) (blue) and tetrameric SxDsbBΔCGZ(C130S) crosslinked to cDsbA(C33A) (red) (b). Radius of gyration (Rg) and maximum particle size (Dmax) are reported for each. Below each envelope is the corresponding crystal structure (PDB 1a23 for monomeric DsbA, PDB 1u3a for dimeric DsbA, PDB 2k74 for monomeric DsbB, PDB 2leg for the complex DsbB(C130S) and DsbA(C33A), PDB 2a01 for ApoAI and 1NL5 for MBP). For each construct, the mathematical representation of the fit for the corresponding crystal structure and its calculated envelope (log intensity, I(q), versus q) is plotted in Supplementary Fig. 6.
