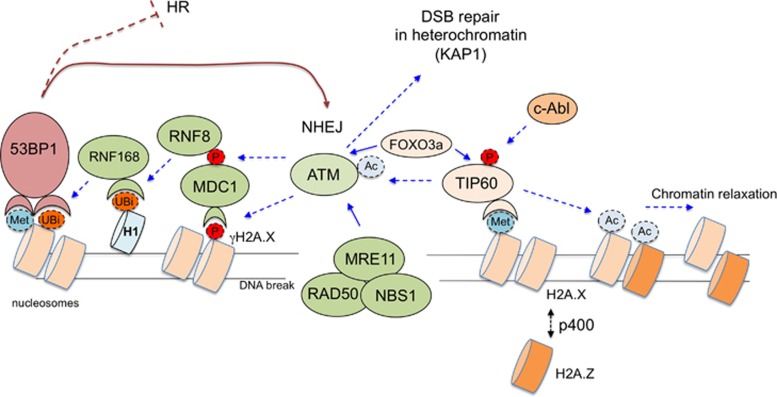
Figure 1.
A simplified scheme of chromatin changes in response to double-strand break (DSB) occurrence highlighting a central role of the ATM kinase. DSBs are recognized by the MRN complex (MRE11; RAD50; NBS1), which leads to activation of the ATM kinase.111 In parallel DNA damage-induced chromatin changes lead to c-Abl tyrosine kinase activation. C-Abl phosphorylates TIP60 (also known as KAT5) acetyltrasferase, which acetylates ATM to elicit full activation of this kinase.112 Interaction between ATM and TIP60 is facilitated by FOXO3A transcription factor.60 Binding of TIP60 to methylated histones (predominantly H3K9me3) is required for its action on ATM and other histone substrates (e.g., H4). TIP60 acetylates histones leading to the formation of open relaxed chromatin structure.18 This step is facilitated by p400 histone chaperone-mediated variant histone exchange at DSBs (H2A.X is replaced by HA2.Z) occurring in close proximity to DSBs (up to ca 3,5 kb away from a DSB).39 The main substrate of ATM kinase is histone H2A.X and phospho-H2A.X (termed γH2A.X) spreads away from the DSBs into megabase sized domains.113 Phospho-H2A.X is recognized by MDC1 adapter protein, which is also the substrate of ATM.114, 115 Phospho-MDC1 in turn recruits RNF8 ubiquitin ligase.116 Linker histone H1 is the main substrate of RNF8 and ubiquitinated H1 is recognized by RNF168 ubiquitin ligase.117 RNF168 ubiquitinates histone H2A on K13/15, which facilitates recruitment of the key adapter protein 53BP1.118 Stable binding of 53BP1 also requires its association with methylated histone H4 (K20me2).119, 120 Of note histone methylation is a constitutive chromatin mark, whereas both histone acetylation and ubiquitination are dynamic DNA damage-induced modifications.121 53BP1 serves as critical regulation of DSB repair pathway choice and promotes NHEJ repair by inhibiting DNA resection (a critical step in homologous recombination (HR) repair).122 ATM is also implicated in the repair of heterochromatin DSBs by phosphorylating KAP1 protein, which in turn promotes opening of heterochromatin to allow for the access of the DNA repair machinery.123