Fig. 1.
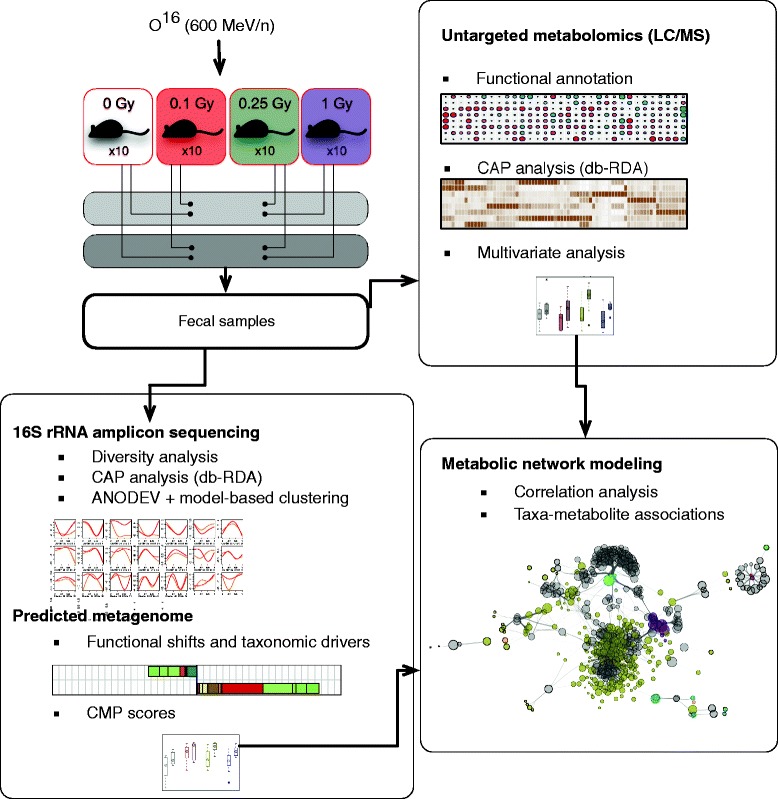
Experimental and analytical design. Fecal samples were collected from irradiated mice and processed for both 16S rRNA amplicon and LC-MS profiling. 16S rRNA amplicon data was analyzed at the phylotype level unless stated otherwise. Constrained Analysis of Principal Coordinates (CAP) provided condition-specific phylotypes and metabolites, while model-based clustering produced a classification of highly responsive phylotypes based on overall response to irradiation. The predicted metagenome was employed to estimate contributions of bacterial phylotypes to significant functional shifts and community-wide metabolic potential (CMP) scores. Metabolic network modeling was used to integrate the 16S rRNA amplicon and metabolomics data and to establish significant associations between phylotypes and metabolic shifts
