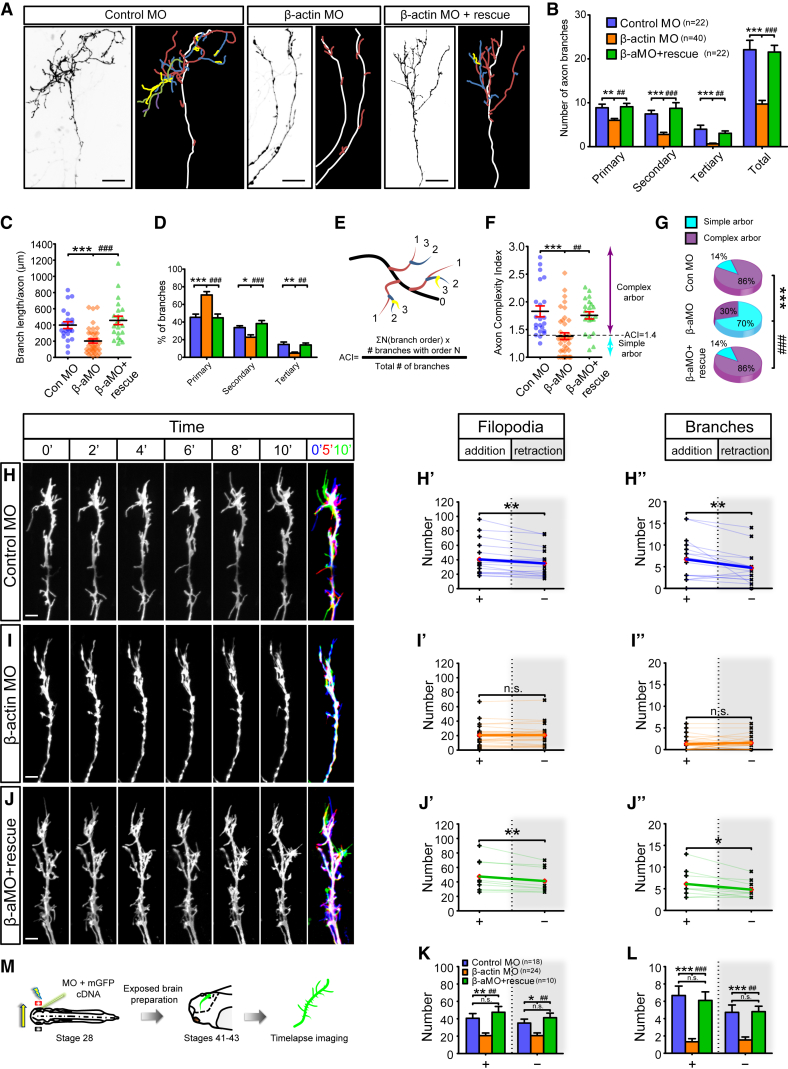
Figure 4.
Knockdown of β-actin Reduces Axon Branching Dynamics and Arbor Complexity In Vivo
(A) Lateral view of single RGC axons in the tectum. Line drawings are shown with the branch order color coded: white, axon shaft; branches: red, primary; blue, secondary; yellow, tertiary; purple, quaternary.
(B) Reduction in number of branches in β-actin morphants (primary: F2,81 = 8.9, p = 0.0003; secondary: F2,81 = 17.6, p < 0.0001; tertiary: F2,81 = 13.0, p < 0.0001; total: F2,81 = 29.3, p < 0.0001).
(C) Branch length decreased in the β-actin MO (β-aMO) condition (F2,81 = 14.69, p < 0.0001).
(D) The proportion of branches in the β-aMO condition shifts toward lower branch orders (primary: F2,81 = 2.1, p < 0.0001; secondary: F2,81 = 4.7, p = 0.0006; tertiary: F2,81 = 4.2, p = 0.0002).
(E) Formulation of axon complexity index (ACI).
(F) The ACI was reduced in the β-aMO condition (F2,81 = 12.0, p < 0.0001).
(G) The percentage of complex arbor (ACI ≥ 1.4) was reduced in β-aMO condition (∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ###p < 0.0001, Fisher’s exact test).
(H–J) Axon branching in Con MO- (H) and β-aMO-positive (I) (+/– rescue construct; J) axons in the tectum. More protrusions were added than removed in control morphants (filopodia: t17 = 3.9, p = 0.0011; branches: t17 = 3.2, p = 0.0049) (H′ and H″). No significant differences were observed in the number of protrusions that were added and removed in β-actin morphants (filopodia: t23 = 0, p = 1; branch: t17 = 0.8, p = 0.42) (I′ and I″). More protrusions were added than removed in β-actin morphants that were rescued with β-aMO resistant construct (filopodia: t9 = 3.5, p = 0.007; branches: t9 = 2.8, p = 0.022) (J′ and J″).
(K and L) The dynamics of filopodia (K; addition: F2,49 = 9.3, p = 0.0004; removal: F2,49 = 6.6, p = 0.003) and branches (L; addition: F2,49 = 16.1, p < 0.0001; removal: F2,49 = 10.2, p = 0.0002) were inhibited in β-actin morphants.
(M) Eye electroporation and live imaging of axonal branching.
Error bars represent SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons test for B–F, K, and L) and paired t test for H–J). Red diamonds represent the averages (H–J). Scale bars, 20 μm for (A) and 5 μm for (H–J). See also Figure S5.