Figure 2.
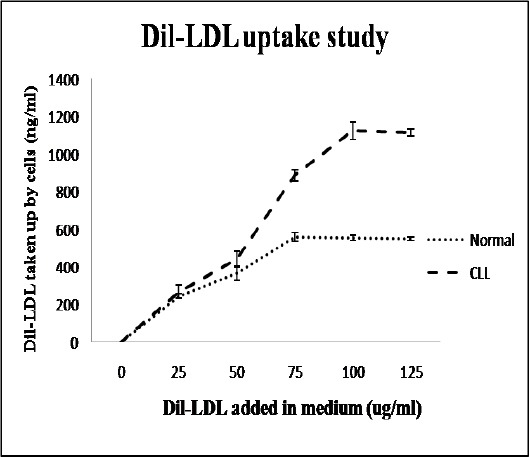
Functional Activity of LDLR by Dil-LDL Uptake Assay: For this assay, 2 x 106 cells/ml were incubated with different concentrations of Dil-LDL (0, 25, 50, 75, 100, 125 µg/ml) for 5 hr in a multi-well plate. Amount of Dil internalized into the cells was proportional to the quantity of LDL taken up by the cells. The graphs show a higher rate of LDL uptake by leukemic lymphocytes as compared to normal counterparts. It was also evident that leukemic lymphocytes required more LDL particles than normal lymphocytes to reach the saturation point. A 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test was employed to determine statistical significance. The data show the mean ± SD for 25 samples from each respective category
