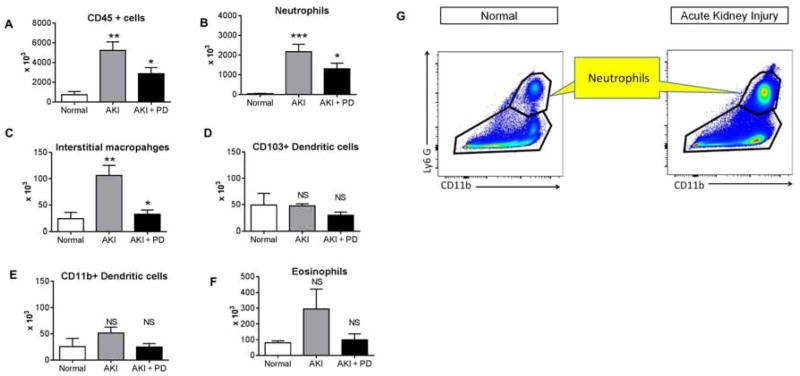
Figure 8. Effect of high dose (HD) peritoneal dialysis (PD) in ischemic AKI on lung leukocyte infiltration as assessed by flow cytometry.
High dose peritoneal dialysis (PD) was performed one hour after ischemic AKI (AKI) for 4 hours with peritoneal dialysate exchanges occurring every 15 minutes [i.e., 4 exchanges per hour for four hours for a total of 16 exchanges]. Normal mice, and mice 5 hours after ischemic AKI were also studied. Flow cytometry was performed on the entire lung and A) CD45+ cells; B) Neutrophils, C) Interstitial macrophages, D) CD103+ Dendritic cells; E) CD11b+ Dendritic cells, and F) Eosinophils were determined. CD45+ cells, neutrophils and interstitial macrophages were significantly reduced in mice with peritoneal dialysis. G) Representative gating strategy for neutrophil detection. (n= normal (4), AKI (9), AKI + PD (9). *P<0.05 versus AKI; ** P<0.01 vs. Normal; *** P<0.001 versus Normal; NS = not significant versus Normal or AKI; one way ANOVA with Dunnet’s post hoc procedure with AKI as the comparison group. Group numbers are Normal: n=4; AKI: n=9; AKI + PD: n=9.