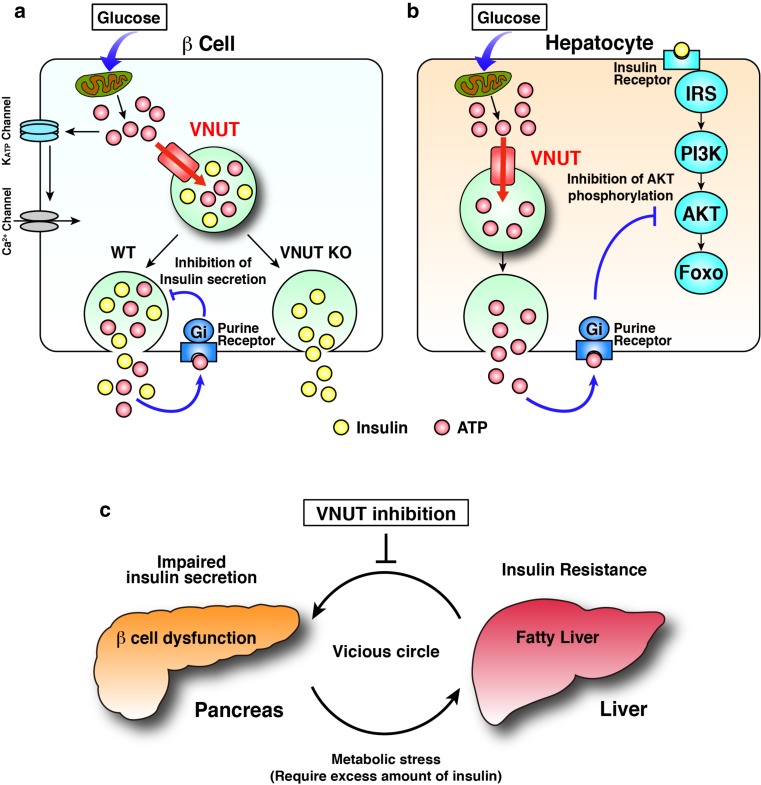
Fig. 5.
Roles of VNUT in the blood glucose homeostasis. a ATP inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion through purinergic signaling. b ATP is secreted from hepatocytes in response to glucose stimulation and, in turn, inhibits AKT phosphorylation through purinergic signaling. c Impaired insulin secretion from pancreas β cells and hepatic insulin resistance yield a vicious circle accelerating the decrease in glucose metabolism. Shutting down the purinergic chemical transmission by inhibiting VNUT breaks this vicious circle. For details, see ref. [86]