Figure 2.
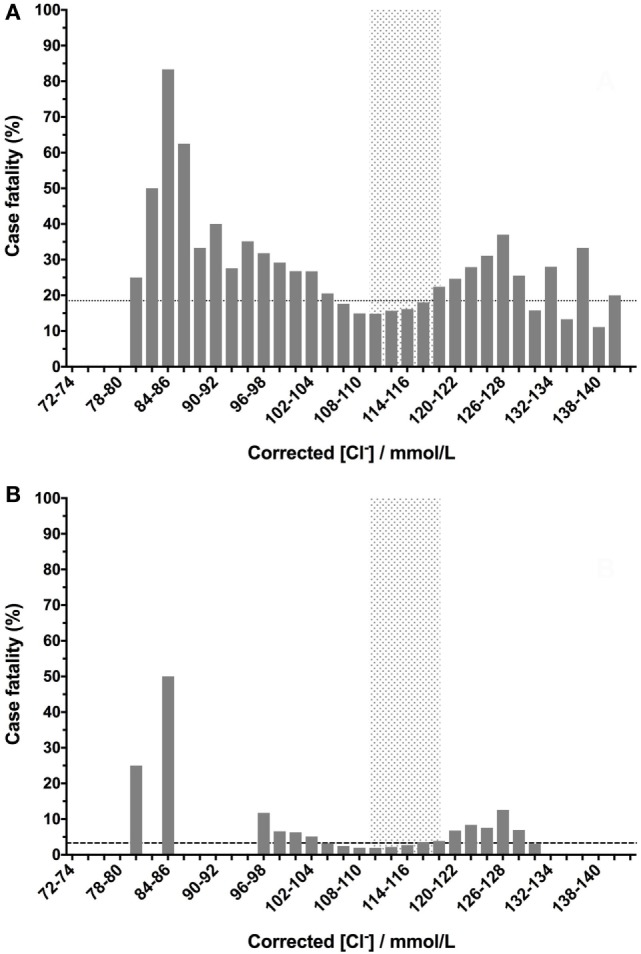
Canine corrected blood chloride concentrations have a U-shaped relationship with case fatality rates. Chloride values were corrected for sodium concentrations as follows: [Cl−]Corrected = [Na+]Normal/[Na+]Measured × [Cl−]Measured. Low- or high-corrected chloride concentrations are associated with increased case fatality rates. Corrected chloride values were banded into 2 mmol/L bins, and the percentage case fatality for the patients in each of these subgroups was calculated. The dotted lines denote the case fatality rate across the entire data set (the background case fatality rate). Panel (A) represents data from all samples (n = 33,117), including those from patients that were euthanized, while panel (B) represents data from patients that survived or died only (i.e., euthanized patients were excluded) (n = 27,904).
