Fig. 3.
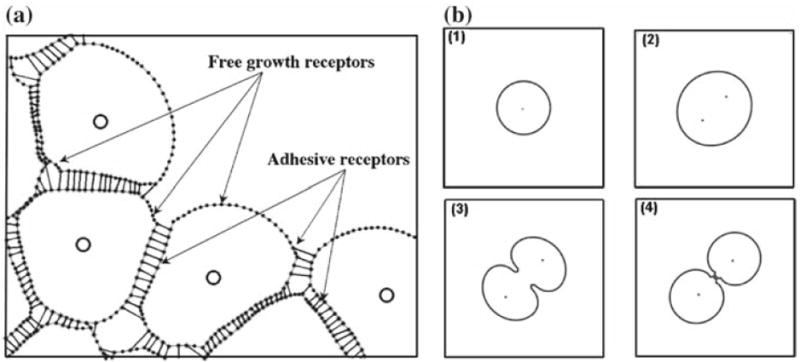
a A portion of a small cluster of adherent cells in the IBCell model. Cell boundary points (dots) are connected by short linear springs to form cell membranes (grey lines); cell nuclei (circles) are located inside cells and are surrounded by cell cytoplasm modelled as a viscous incompressible Newtonian fluid; separate cells are connected by adherent links (thin black lines); growing cells acquire the fluid from the extracellular space through the free membrane receptors. b Morphological alterations in a proliferating cell: 1 a cell ready to grow, 2 an enlarged growing cell with two daughter nuclei, 3 formation of the contractile ring orthogonal to the cell longest axis, 4 cellular division into two daughter cells of approximately equal areas
