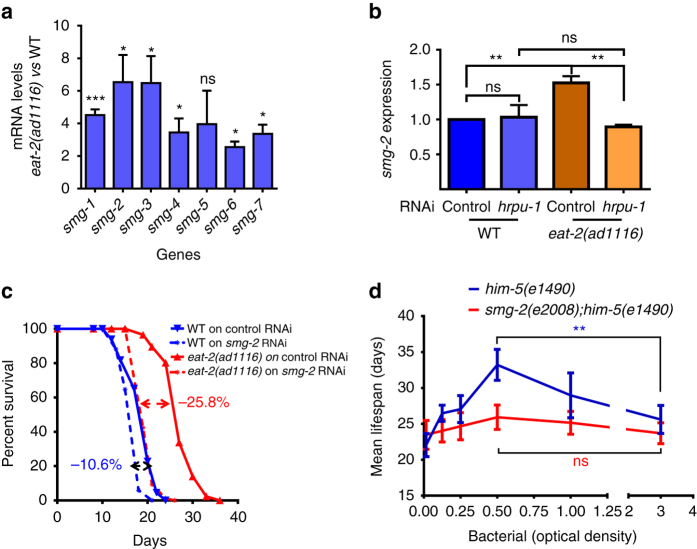
Fig. 4.
MRNA surveillance pathway is upregulated and required for DR-mediated longevity. a qRT-PCR showing that genes of NMD pathway are upregulated in eat-2(ad1116) at day 1 of adulthood. Expression levels were normalized to actin and compared to WT worms. Averages of three biological replicates are shown (Error bars = SEM). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences to the corresponding WT samples, as calculated by unpaired two-tailed t-test (*P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ns non-significant). b The expression of smg-2 is upregulated in eat-2(ad1116) compared to WT, in a hrpu-1-dependent manner. The samples were collected on day 3 of adulthood. Data shown are average of three biological replicates. (Error bars = SEM). Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired two-tailed t-test. **P ≤ 0.01, ns non-significant. c Lifespan of WT and eat-2(ad1116) grown on control or smg-2 RNAi. One out of the three biological replicates are shown. Percentage of suppression of lifespan is indicated for each strain. Lifespan data for each individual experiment are provided in Supplementary Table 4. d Bell-shaped curve generated by plotting average lifespans of him-5(e1490) grown in the presence of different dilutions of bacteria. The smg-2(e2008);him-5(e1490) mutant worms failed to produce similar curve. An average of three independent biological replicates is shown. Error bars are SEM. Two-way ANOVA revealed that the lifespan extension of him-5(e1490) worms across the bacterial dilution range was significantly different from that of smg-2(e2008);him-5(e1490) (P ≤ 0.05). Bacterial culture of OD600 = 3.0 was the starting concentration for serial dilution. Additionally, the increase in lifespan when him-5(-) was maintained at OD600 = 0.5 was significant as compared to OD600 = 3.0; the difference in case of smg-2(-);him-5(-) was not. **P ≤ 0.01, ns non-significant; unpaired two-tailed t-test. All the mean lifespan and statistical analysis are provided in Supplementary Table 4