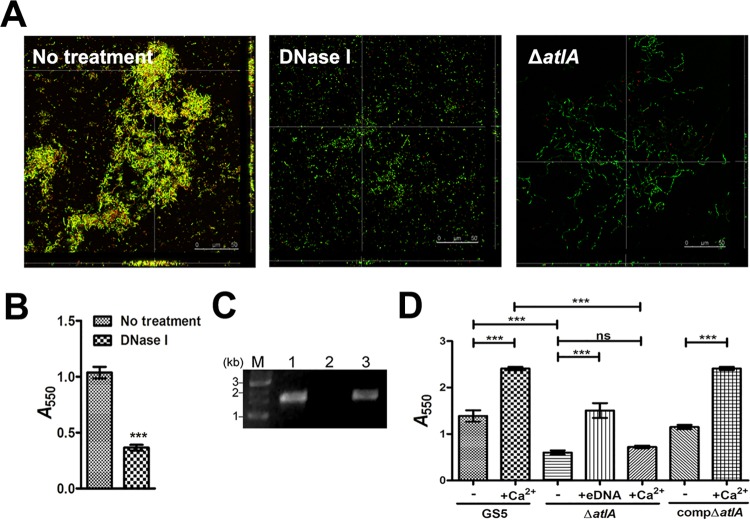
FIG 2.
AtlA mediates bacterial eDNA release and biofilm formation. (A) CLSM images of GFP-tagged wild type S. mutans biofilms grown without (left) and with (center) DNase I and a ΔatlA biofilm (right) stained with 10 μM PI (magnification, ×630). Yellow areas indicate the presence of both S. mutans and eDNA. (B) Biofilms grown in 96-well plates with or without DNase I were stained with 0.1% crystal violet. Staining was detected by measuring the absorbance at 550 nm. Data are means ± standard deviations from triplicate experiments. Asterisks indicate significance (***, P < 0.001) by Student's t test. (C) eDNA released by wild-type (lane 1), ΔatlA (lane 2), and compΔatlA (lane 3) strains was amplified by PCR using bacterial 16S rRNA primers, and the products were resolved on 1% agarose gels. M, marker. (D) Biofilms of wild-type, ΔatlA, and compΔatlA strains were grown with or without purified bacterial eDNA or 0.1 mM calcium ions and were stained with 0.1% crystal violet. Staining was quantified by measuring the absorbance at 550 nm. Data are means ± standard deviations from triplicate experiments. Asterisks indicate significance (***, P ≤ 0.001) by one-way ANOVA. These experiments were repeated three times, and results of a representative experiment are shown.