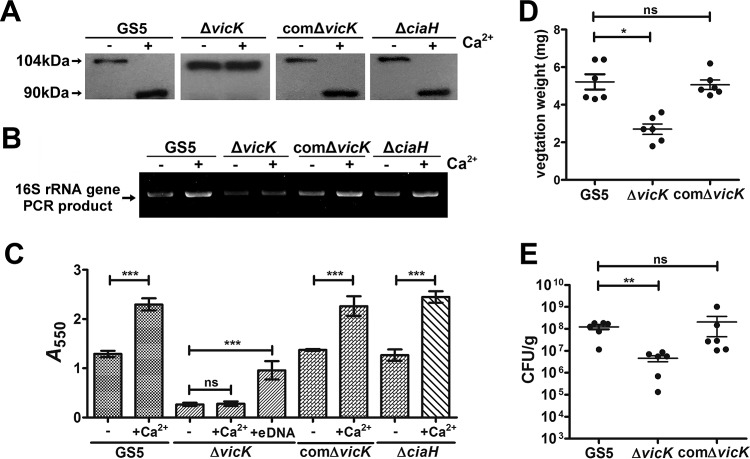
FIG 5.
VicK, but not CiaH, is required for calcium ion sensing, induction of AtlA maturation, bacterial eDNA release, and enhanced biofilm formation. (A) S. mutans GS5, ΔvicK, comΔvicK, and ΔciaH strains were cultured in medium with or without the addition of calcium ions. Bacterial cell wall-associated proteins were isolated by use of 8 M urea and were subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-AtlA antibodies. Calcium ion-enhanced AtlA maturation was abolished in the vicK-deficient strain. (B) eDNA released into the medium of S. mutans GS5, ΔvicK, comΔvicK, and ΔciaH strains cultured with or without 100 μM calcium ions was PCR amplified using bacterial 16S rRNA primers, and products were resolved on 1% agarose gels. (C) The biofilms of S. mutans GS5, ΔvicK, comΔvicK, and ΔciaH strains grown in medium with or without purified bacterial eDNA and/or 0.1 mM calcium ions were stained with 0.1% crystal violet and were quantified by measuring the absorbance at 550 nm. Data are means ± standard deviations from triplicate experiments. Asterisks indicate significance (***, P < 0.001) by one-way ANOVA. These experiments were repeated three times, and results of a representative experiment are shown. (D and E) The role of VicK in the pathogenesis of S. mutans in IE was further investigated using the ΔvicK and comΔvicK strains in a rat model of IE. Vegetation size (D) and the numbers of colonized bacteria inside vegetations (E) were measured. Data represent means ± standard error of the means and were statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's test (**, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05).