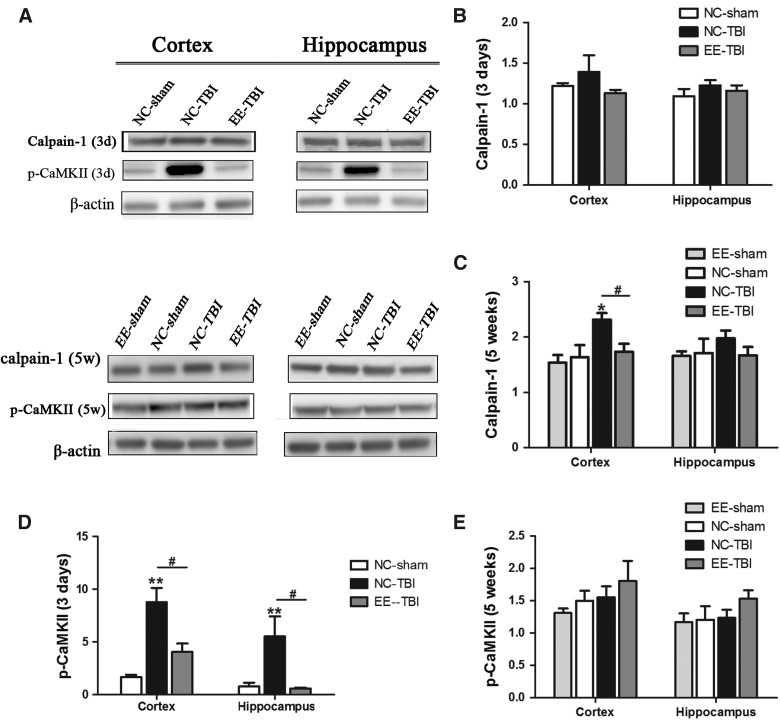
FIG. 2.
Expression of calpain-1 and p-CaMKII. Expression of calpain-1 and phosphorylated CaMKII were analyzed by western blot. (A) Representative images of calpain-1, p-CaMKII, and β-actin. (3d: 3 days after last injury; 5w: 5 weeks after last injury). (B) Semiquantitative analysis of calpain-1 3 days after injury. (C) Semi quantitative analysis of calpain-1 5 weeks after injury (*p < 0.05, NC-TBI vs. NC sham; #p < 0.05, NC-TBI vs. EE-TBI). (D) Semiquantitative analysis of p-CaMKII 3 days after injury and (E) semiquantitative analysis of p-CaMKII, 5 weeks after injury, using densitometry. β-actin was used as the control. Relative expression of each molecule was compared to β-actin expression (#p < 0.05, NC-TBI vs. EE-TBI; **p < 0.01, NC-TBI vs. NC-sham). (E) There was no significant difference in p-CaMKII expression in the cortex and hippocampus between each group, 5 weeks after last injury. EE, environmental enrichment; NC, normal condition; p-CaMKII, phosphorylated Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; TBI, repetitive mild traumatic brain injury.