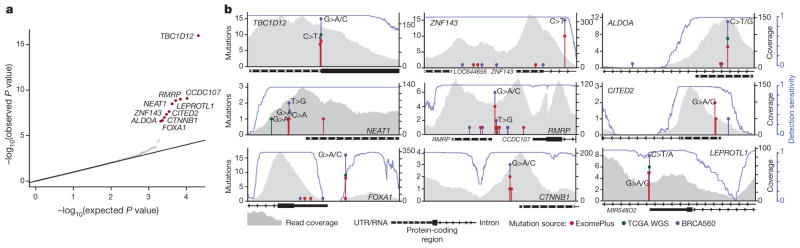
Figure 1. Identification of significantly mutated promoters.
a, Quantile–quantile plot for gene promoter P values. Red dots indicate significantly mutated promoters (Benjamini–Hochberg FDR q <0.1). b, Detailed view of analysed gene loci for significantly mutated promoters including stacked lollipops representing mutations from this study (red), 98 TCGA whole-genome sequencing (WGS) (green), and 560 breast cancer genomes from BRCA560 (ref. 5, purple). Base changes at mutation sites are indicated above mutation count. Grey profiles indicate read coverage from a representative patient. Blue lines depict mutation detection sensitivity at base-level resolution in each promoter region.