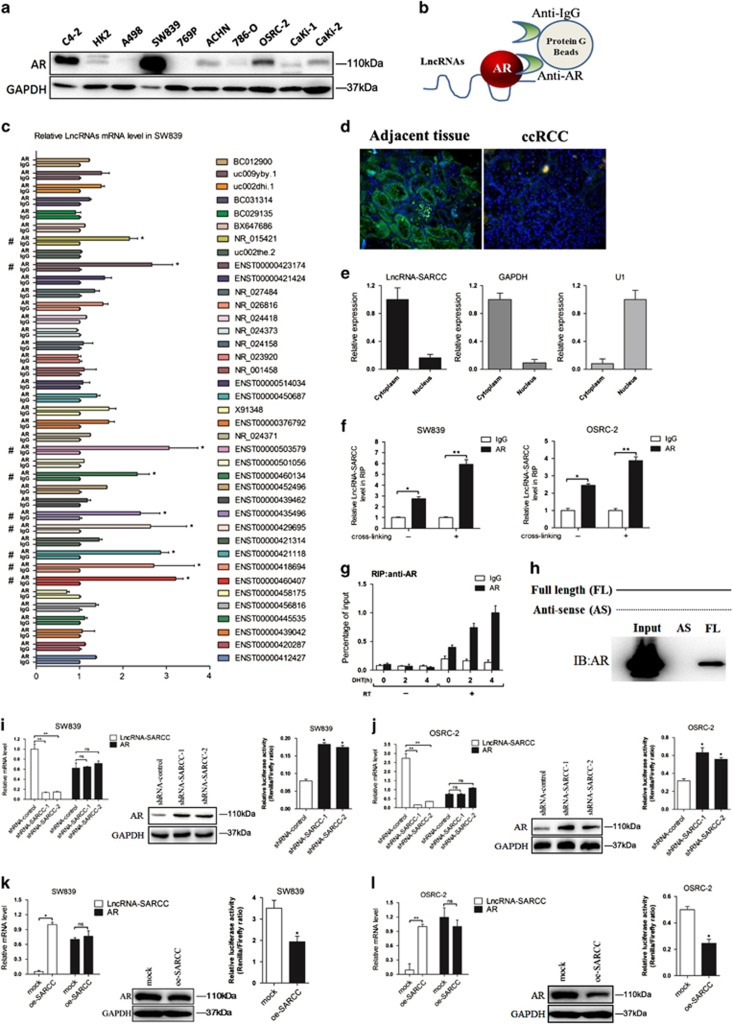
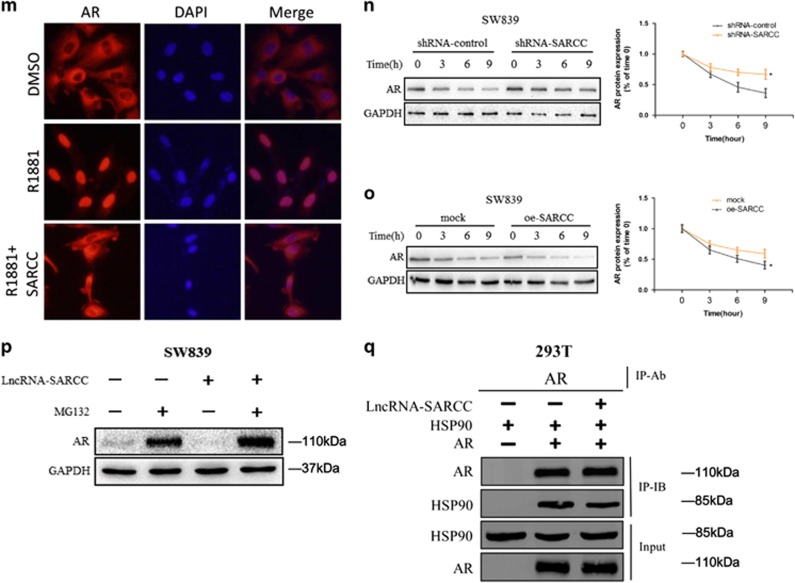
Figure 1.
LncRNA-SARCC is physically associated with and negatively correlated with AR. (a) Immunoblot of AR expression in a series of RCC cell lines or immortalized proximal tubule epithelial cell line from normal adult human kidney (HK2, A498, SW839, 769-P, ACHN, 786-O, OSRC-2, Caki-1 and Caki-2), with prostate cancer cell line C4-2 as positive control. (b) A schematic illustration of the procedure used to discover and define LncRNAs binding to AR in RCC tissues. (c) RIP assays for the potential LncRNA candidates endogenously associated with AR in SW839 cells. Total RNA was subjected to qRT-PCR assays. (d) Primary RCC and adjacent non-cancerous renal tissues were subjected to RNA FISH and analyzed by ultraviolet light excitation using a fluorescence microscope. (e) qRT-PCR for LncRNA-SARCC, GAPDH and U1 from RNA extracted from cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. (f) SW839 and OSRC-2 cells were cross-linked with/without 4% paraformaldehyde before RIP assays were carried out. (g) RIP assay in 10 nM DHT-treated SW839 cells at the indicated time points. (h) RNAs corresponding to different fragments of LncRNA-SARCC were biotinylated and incubated with SW839 cell extracts, targeted with streptavidin beads and washed. Associated AR protein was detected by WB and compared between full length LncRNA-SARCC and its antisense RNA. (i and j) qRT-PCR assays (left panels) for the shRNA-SARCC mRNA level in stable SW839 (i) and OSRC-2 (j) cell clones. AR protein and luciferase level were measured by WB (middle panels) and luciferase reporter assay (right panels). (k and l) qRT-PCR assays for the oe-SARCC mRNA levels in stable SW839 (k) and OSRC-2 (l) cell clones. AR protein and luciferase level were measured by WB (middle panels) and luciferase reporter assay (right panels). (m) Immunofluorescence staining of AR. SW839-control and SW839-LncRNA-SARCC cells were hormone-starved for 3 days and the SW839-control cells treated with DMSO or 1 nM R1881, whereas the SW839-LncRNA-SARCC cells were treated with R1881 for 24 h before subjected to immunostaining using an anti-AR antibody. (n) SW839 cells expressing control shRNA or LncRNA-SARCC shRNA were treated with 20 mg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated time periods and cell lysates analyzed by WB. (o) SW839 cells expressing mock or oe-LncRNA-SARCC were treated as in (n) and analyzed by WB. (p) SW839 cells expressing shRNA-control (−) or shRNA-SARCC (+) were cultured with/without 5 mM MG132 for 10 h and cell lysates analyzed by WB. (q) CoIP showing AR-Hsp90 protein interaction with the absence or presence of LncRNA-SARCC. AR, Hsp90 and LncRNA-SARCC were expressed in 293T cells through transient transfection followed by AR immunoprecipitation. AR and associated Hsp90 protein was detected by immunoblot analysis. Data shown are mean±S.D. (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01