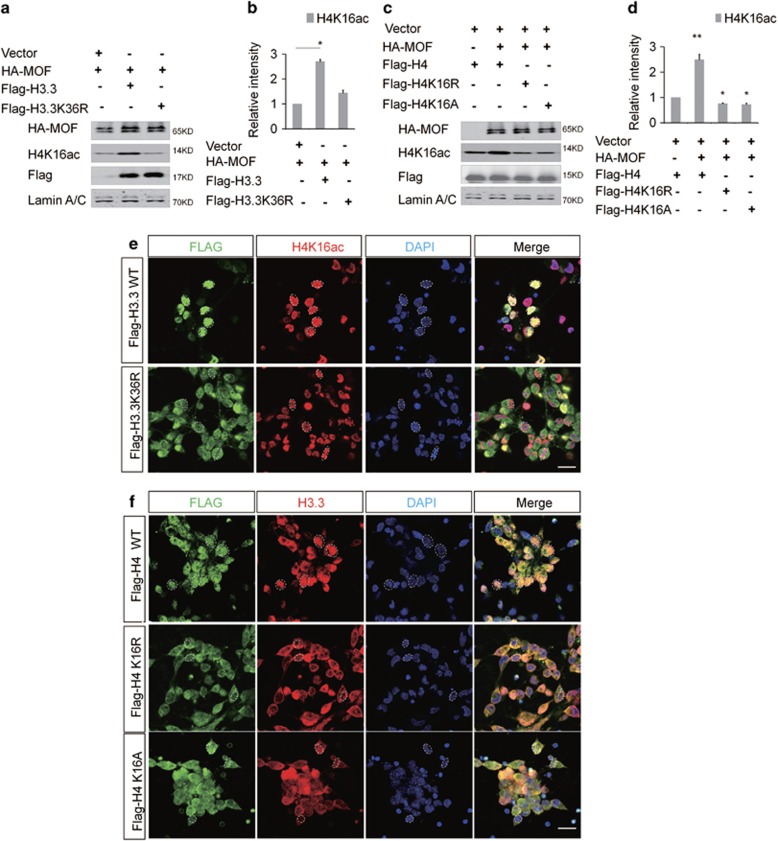
Figure 7.
H3.3K36 and H4K16 Mutation Influence the H4K16 Acetylation. (a, b) H3.3K36R could not promote the acetylation of the H4K16 as H3.3-WT. The indicated viruses were delivered into NSC, and the protein level of H4K16ac was detected (n=3 independent experiments; bar represents mean±S.E.M; **P<0.01; Lamin A/C served as loading control). (c,d) Overexpression of H4K16R or H4K16A could not promote the acetylation of H4K16 in NSCs. The indicated viruses were delivered into NSCs, and the protein level of H4K16ac was detected (n=3 independent experiments; bar represents mean±S.E.M; **P<0.01; Lamin A/C served as loading control). (e) Abnormal distribution of Flag-H3.3K36R decreases the fluorescence intensity of the H4K16ac in NSCs versus the Flag-H3.3WT. (f) Abnormal distribution of Flag-H4K16R (or H4K16A) versus the Flag-H4WT