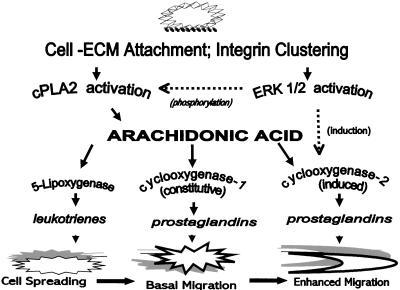
Figure 11.
Model of a bifurcated arachidonic acid pathway regulating a transition from cell spreading to cell migration. NIH-3T3 cell spreading on fibronectin is by means of α5β1-integrin receptors in the plasma membrane initially binding extracellular matrix fibronectin. The signaling pathway begins with integrin receptor clustering during cell-ECM attachment, which stimulates rapid cPLA2 activation and an immediate transient AA release oxidized by 5-lipoxygenase, generating leukotrienes to signal cell spreading. ERK1/2 is also rapidly activated during the cell attachment phase, and modulates cPLA2 activity to enhance a later sustained AA release, as well as inducing the immediate expression of COX-2 protein. Up-regulation of COX-2 increases total prostaglandin production over that contributed by constitutive COX-1, to stimulate a postspreading transition to migration.