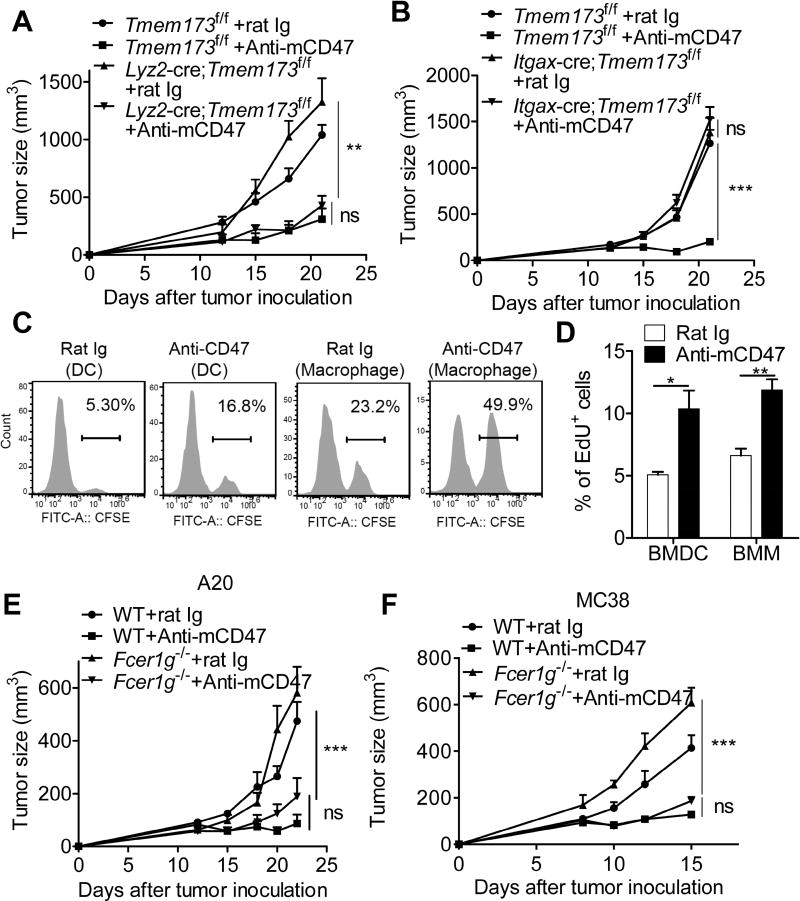
Figure 1. The therapeutic effect of anti-CD47 mAb depends on cytosolic DNA sensing pathway in DCs, but not in macrophage.
(A–B) Tmem173fl/fl (n=5), Lyz2-cre;Tmem173fl/fl mice (n = 5) and Itgax-cre;Tmem173fl/fl mice (n = 5) were injected s.c. with 1 × 106 MC38 cells and treated with 50 µg of anti-CD47 or rat Ig on days 12 and 15. (C) CFSE-labeled MC38 tumor cells were co-cultured with bone marrow-derived DCs (BMDC) or macrophages (BMM) for one hour in the presence of 30µg/ml rat Ig or anti-CD47 mAb. (D) EdU-labeled MC38 tumor cells were co-cultured with BMDC or BMM for four hours in the presence of 30µg/ml rat Ig or anti-CD47 mAb. Percentage of EdU positive BMDC and BMM were quantified. (E) WT mice or Fcer1g−/− mice (n = 5 mice/group) were injected s.c. with 3×106 A20 cells and treated i.t. with 50 µg of anti-CD47 or rat Ig on days 12 and 15. (F) WT mice or Fcer1g−/− mice (n = 5 mice/group) were injected s.c. with 1×106 MC38 cells and treated i.t. with 50 µg of anti-CD47 or rat Ig on days 8 and 10. Data are representatives of two (A, B, E and F) or three (C, D) independent experiments and presented as mean ± SEM. * p< 0.05, ** p< 0.01, *** p< 0.001 (Two-tailed student’s t test). See also Figure S1.