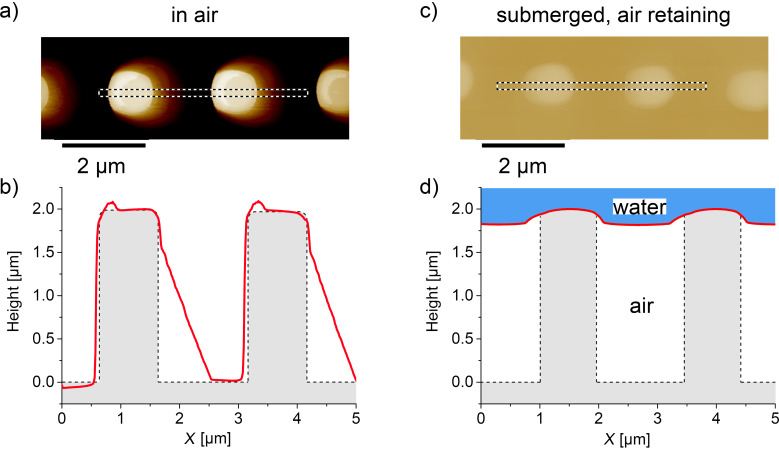
Figure 5.
AFM images (a, c) and the corresponding cross-sections (red lines in b, d) of the sample. The image in a) was taken in ambient conditions in tapping mode and confirms the pillar height of 2 µm. The light coloration on the right side of each pillar is an unavoidable artifact in AFM imaging, originating from the pyramidal shape of the AFM tip. This is also displayed by the corresponding cross section (red line) in b). The actual topography is also schematically illustrated (grey). c) AFM image taken in contact mode of a submerged air-retaining sample. d) The red line shows the cross-section with a total height of only 185 nm. Hence the AFM tip does not reach the base of the sample but rather follows the air–water interface, which is 185 nm below the pillar tops. The height of the air layer beneath is 1.815 µm, which translates to at least 90% of the total pillar height.