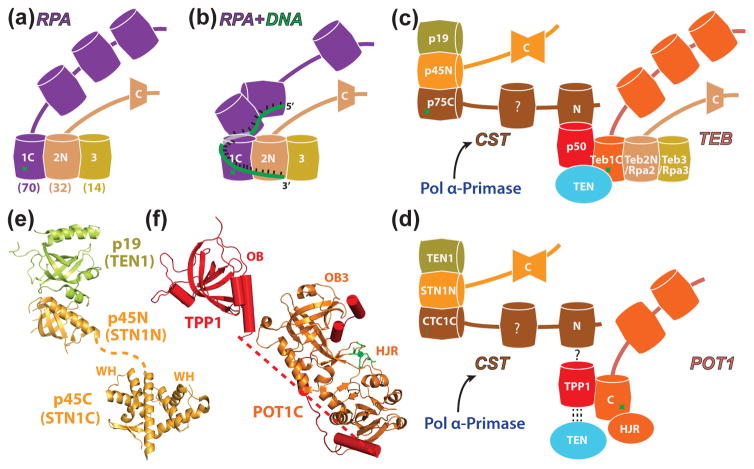
Figure 4.
RPA, TEB, CST and their interactions. (a) Schematic of the RPA heterotrimer of Rpa1-Rpa2-Rpa3 (Rpa70, 32, and 14 in humans). Shared subunits Teb2/Rpa2 and Teb3/Rpa3 found in Tetrahymena are indicated by common colors with panel c. (b) Schematic of the structure of a RPA-ssDNA complex, based on [81]. (c) Schematic of the two RPA-like complexes, CST (p75-p45-p19) and TEB (Teb1-Teb2-Teb3), in Tetrahymena telomerase and their interactions with p50 and TEN domain; (d) Schematic of the two RPA-like complexes/proteins that transiently associate with human telomerase, CST (CTC1-Stn1-Ten1) and Pot1 (paralog of Rpa1), their interaction with TPP1 (putative for CTC1), and the interaction of TPP1 with the TEN domain. The human telomerase RNP core is recruited to telomere by TPP1-POT. CST interaction with TPP1-POT1 inhibits telomerase activity; (e,f) Crystal structures of (e) p45N-p19 complex (PDB ID: 5DOI) and p45C domain (PDB ID: 5DFN) and (f) POT1C-TPP1 complex which is modeled based on crystal structures of POT1C-TPP1 PBM complex (PDB ID: 5UN7), TPP1 (PDB ID: 2I46), and TEBPα–β–ssDNA complex (PDB ID: 1OTC) [65]. In (a-d), barrels indicate OB-fold domains, single trapezoid is WH domain, double trapezoid is tandem WH-WH domains, green star is a zinc-binding motif. Homologous domains for Tetrahymena and human telomerase/telomere proteins are colored the same (c-d); for RPA (a, b) the two smaller subunits are identical with those of TEB.