Abstract
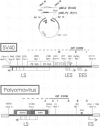
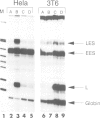
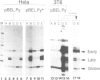
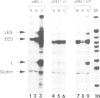
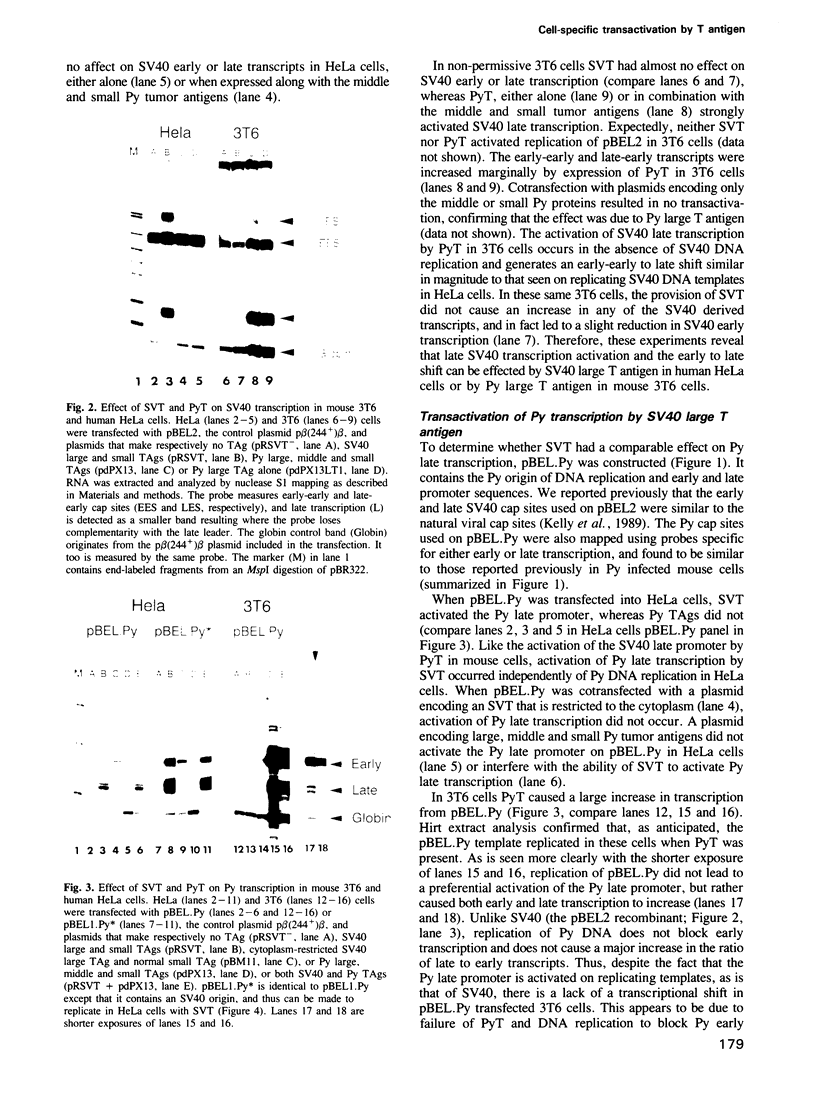
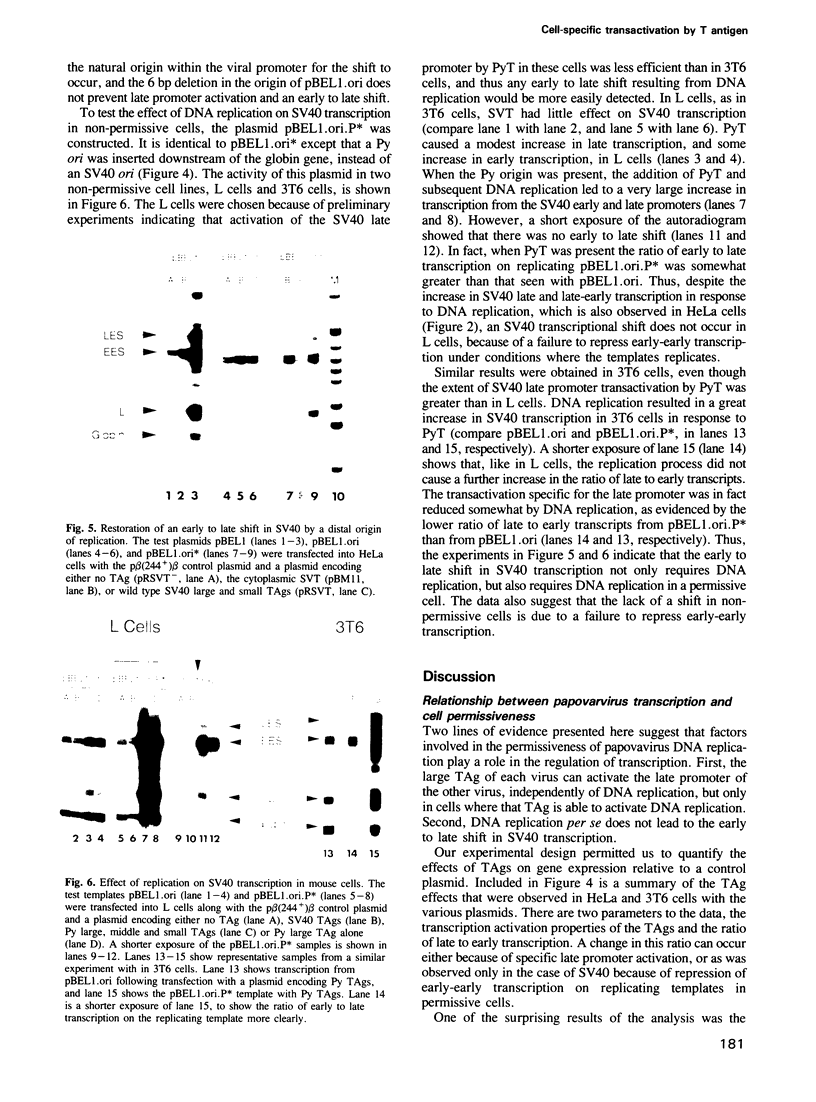
Simian virus 40 (SV40) and polyomavirus (Py) DNA replication require cellular proteins and a virus-encoded early gene product, large T antigen (SVT and PyT, respectively). Primate cells contain factors permissive for SV40 replication, whereas murine cells express those factors permissive for Py. We have compared the roles T antigen, cell permissiveness and replication play in transcription of SV40 and Py genes. We show that in their respectively permissive cells, SV40 replication causes a major shift in transcription initiation from the early to the late viral promoter, whereas when Py replicates a comparable shift does not occur. This difference is discussed in relation to differences in the organization of the origin and promoter region between these two papovaviruses. Reporter plasmids were constructed that carried both viral origins, one at the natural position in the promoter being tested and the other at a distal location. With the appropriate TAg, these vectors could be made to replicate in either primate (HeLa) or rodent (3T6) cells. The SV40 early to late shift occurred when replication was driven in HeLa cells, and was not seen on replicating templates in rodent cells. Thus, replication per se does not account for the shift. We show also that, like SVT, PyT is a potent activator of transcription, and that SVT and PyT can activate each other's late promoters independently of DNA replication, but only in cells permissive for DNA replication catalysed by the respective T antigen. Taken together, the data presented here suggest that papovaviruses may utilize permissive factors in transcription control mechanisms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H. Polyoma virus giant RNAs contain tandem repeats of the nucleotide sequence of the entire viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4754–4758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati P. Polyoma regulatory region: a potential probe for mouse cell differentiation. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):561–562. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90225-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera-Saldana H., Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Wildeman A., Davidson I., Chambon P. All six GC-motifs of the SV40 early upstream element contribute to promoter activity in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3839–3849. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04156.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett-Cook E. R., Hassell J. A. Activation of polyomavirus DNA replication by yeast GAL4 is dependent on its transcriptional activation domains. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):959–969. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Bolen J. B., Radonovich M., Salzman N., Khoury G. Stimulation of simian virus 40 late gene expression by simian virus 40 tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Khoury G. trans Activation of the simian virus 40 late transcription unit by T-antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Loeken M. R., Khoury G. Interaction between two transcriptional control sequences required for tumor-antigen-mediated simian virus 40 late gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7299–7303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Sturzbecher H. W., Addison C., Palmer C., Rudge K., Jenkins J. R. Mouse p53 inhibits SV40 origin-dependent DNA replication. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):458–460. doi: 10.1038/329458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill K. B., Roome A. J., Carmichael G. G. Replication-dependent transactivation of the polyomavirus late promoter. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):992–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.992-1001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. A., Villarreal L. P. Lymphoid and other tissue-specific phenotypes of polyomavirus enhancer recombinants: positive and negative combinational effects on enhancer specificity and activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2068–2079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng L., Kelly T. J. Transcriptional activator nuclear factor I stimulates the replication of SV40 minichromosomes in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):541–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colledge W. H., Richardson W. D., Edge M. D., Smith A. E. Extensive mutagenesis of the nuclear location signal of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4136–4139. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Kamen R. Multiple binding sites for polyomavirus large T antigen within regulatory sequences of polyomavirus DNA. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):750–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.750-760.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Deb S., Partin K., Tegtmeyer P. Functional interactions of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication with flanking regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.138-144.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M., Dean F. B., Bullock P., Echols H., Hurwitz J. Unwinding of duplex DNA from the SV40 origin of replication by T antigen. Science. 1987 Nov 13;238(4829):964–967. doi: 10.1126/science.2823389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Höss A., Arthur A. K., Fanning E. SV40 T antigen binds directly to the large subunit of purified DNA polymerase alpha. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3329–3336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmerie W. G., Folk W. R. Regulation of polyomavirus transcription by large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6919–6923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. J., Gruda M. C., Manuppello J. R., Alwine J. C. Activity of simian DNA-binding factors is altered in the presence of simian virus 40 (SV40) early proteins: characterization of factors binding to elements involved in activation of the SV40 late promoter. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):173–184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.173-184.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Tyndall C., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The high affinity binding site on polyoma virus DNA for the viral large-T protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5697–5710. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's contain multiple 5' termini upstream and downstream from a Hogness-Goldberg sequence; a shift in 5' termini during the lytic cycle is mediated by large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):224–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.224-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Frisque R. J., Sambrook J. Origin-defective mutants of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):293–300. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Sharp P. A. T antigen repression of SV40 early transcription from two promoters. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz G. Z., Mertz J. E. Bidirectional promoter elements of simian virus 40 are required for efficient replication of the viral DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3513–3522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde-DeRuyscher R. P., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus late pre-mRNA processing: DNA replication-associated changes in leader exon multiplicity suggest a role for leader-to-leader splicing in the early-late switch. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5823–5832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5823-5832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde-DeRuyscher R., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus early-late switch is not regulated at the level of transcription initiation and is associated with changes in RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8993–8997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Essential contact residues within SV40 large T antigen binding sites I and II identified by alkylation-interference. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Analysis of an activatable promoter: sequences in the simian virus 40 late promoter required for T-antigen-mediated trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1859–1869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. J., Munholland J. M., Wildeman A. G. Comeasurement of simian virus 40 early and late promoter activity in HeLa and 293 cells in the presence of T antigen. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):383–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.383-391.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Clancy S., Calos M. P. Simian virus 40 replication in adenovirus-transformed human cells antagonizes gene expression. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):169–171. doi: 10.1038/317169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Chen G. J., Woodworth-Gutai M. Simian virus 40 DNA replication: functional organization of regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3086–3093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. D., Manley J. L. Repression of simian virus 40 early transcription by viral DNA replication in human 293 cells. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):172–175. doi: 10.1038/317172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Peden K. W., Dixon R. A., Kelly T. Functional organization of the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1117–1128. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Muller W. J., Hassell J. A. The polyomavirus enhancer comprises multiple functional elements. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1667–1678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1667-1678.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Dufort D., Hassell J. A. Multiple subelements within the polyomavirus enhancer function synergistically to activate DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5000–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Eki T., Yamada M., Prives C., Hurwitz J. Species-specific in vitro synthesis of DNA containing the polyoma virus origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Role of DNA polymerase alpha and DNA primase in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2869–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz B. J., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus and simian virus 40 large T antigens bind to common DNA sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):925–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.925-937.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher B. M., Dean D. H., Garro A. J. Fragmentation of Bacillus bacteriophage phi105 DNA by complementary single-stranded DNA in the cohesive ends of the molecule. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):377–383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.377-383.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Brain R., Maimets T., Addison C., Rudge K., Jenkins J. R. Mouse p53 blocks SV40 DNA replication in vitro and downregulates T antigen DNA helicase activity. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):405–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Kamen R. Structure of polyoma virus late nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):273–301. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Transcription from the SV40 early-early and late-early overlapping promoters in the absence of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G. Transactivation of both early and late simian virus 40 promoters by large tumor antigen does not require nuclear localization of the protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2123–2127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: large-tumor-antigen- and origin-dependent unwinding of the template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]