Figure 5. GBK induces apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
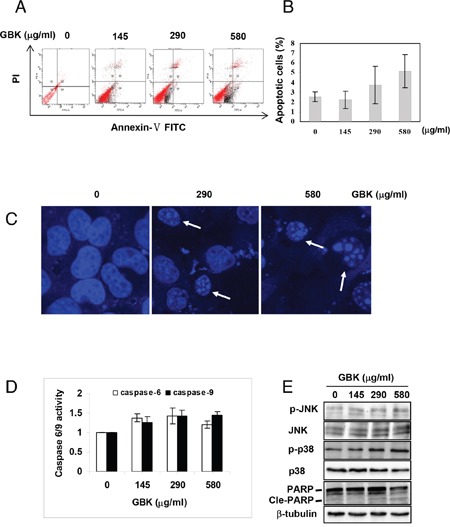
(A, B) Induction of apoptosis in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells was determined by flow cytometry after treatment with GBK (0–580 μg/ml) for 48 h. Representative flow cytometry data is shown in (A), and columns in (B) show the data expressed as means ± SD of three independent experiments. (C) GBK treatment induced apoptotic morphology in MCF-7 cells. MCF-7 cells were treated with GBK (0–580 μg/ml) for 48 h. Cell morphology was observed using a confocal microscope (Zeiss) after Hoechst 33258 staining. White arrows indicate the fragmented DNA in apoptotic cells. (D) GBK induced a dose-dependent activation of caspase 6 and caspase 9. MCF-7 cells were treated with GBK (0–580 μg/ml) for 48 h, and the activations of caspase 6 and caspase 9 were measured by ELISA. Columns show the data expressed as means ± SD of three independent experiments. (E) After treated with 0–580 μg/ml GBK for 24 h, the phosphorylation status of JNK (or p38 MAPK) and the apoptosis-associated protein expression of cleave PARP were detected using western blot. β-tubulin was used as internal control.
