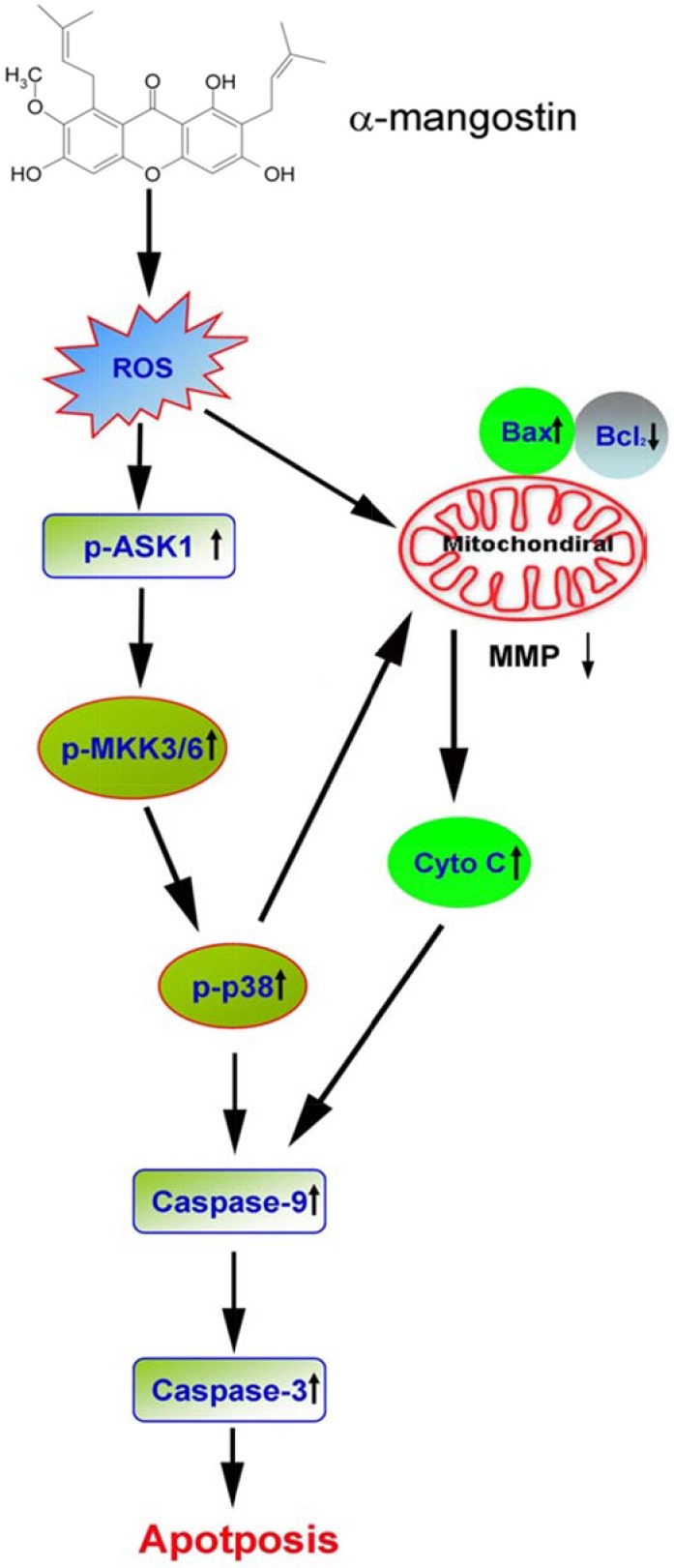
Figure 8. A proposed model of α-mangostin-induced apoptosis in cervical cancer.
The scheme illustrates the proposed mechanism of α-mangostin-induced apoptosis in cervical cancer. Alpha-mangostin enhances ROS content to activate ASK/p38 signaling pathway and damage the integrity of mitochondria, including loss of MMP, increase of Bax and cytochrome C release, and decrease of Bcl-2, leading to activation of caspase-9/caspase-3 cascade and induction of apoptosis in cervical cancer cells.