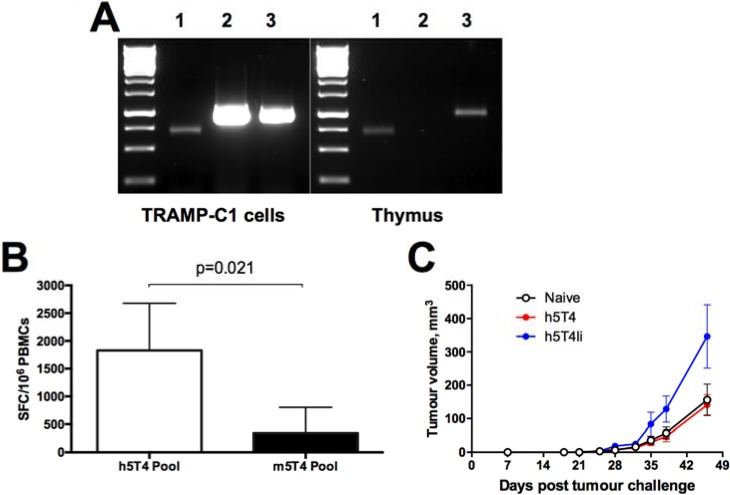
Figure 2. Immune responses induced against human 5T4 antigen do not protect against tumours expressing murine 5T4 despite in vitro cross-reactivity.
(A) Expression of murine 5T4 on transcriptional level in TRAMP-C1 cells and murine thymus by PCR. After total RNA extraction, RT-PCR with primers specific for β-actin (lane 1), STEAP1 (lane 2) and m5T4 (lane 3), was performed. (B) Cross-reactivity with m5T4 protein of h5T4 specific murine T cells. Blood samples were collected from mice vaccinated with 108 IU of ChAdOx1.h5T4 followed by 107 pfu of MVA.h5T4; PBMCs were stimulated with h5T4 or m5T4 peptide pools and tested by ELIspot assay. Bars represent mean responses + SD. (C) C57BL/6 male mice were injected subcutaneously with TRAMP-C1 cells and randomised into three groups. The first group received GFP vaccination (naïve) and the second and third groups received h5T4 and h5T4Ii encoding vaccines, respectively. Tumour size was measured three times per week and volumes were calculated via the equation (a2*b)*0.52. Kinetics of tumour growth for each group are expressed by mean tumour volume ± SEM. Data from one representative experiment are shown.