Figure 5. ATP6V1C1 is highly expressed in human breast cancer cells, and ATP6V1C1 knockdown inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation and mTORC1 pathway activation stimulated by amino acids.
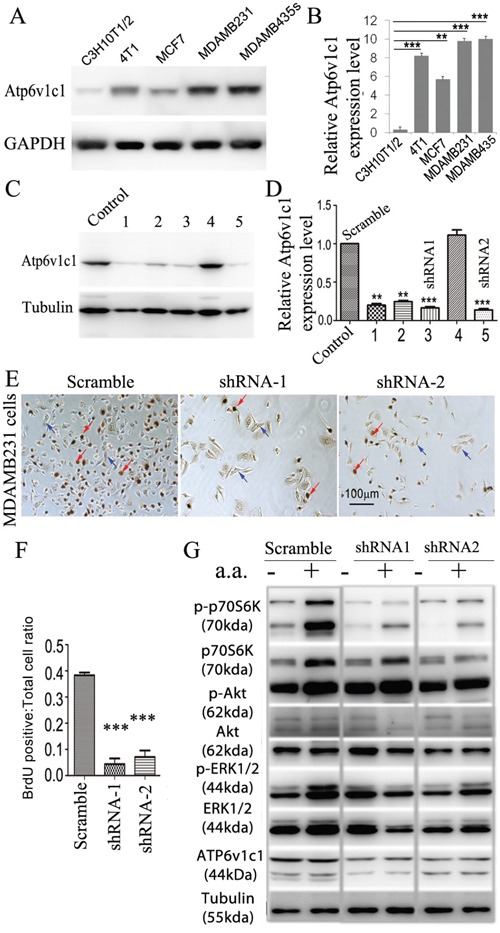
A. Western blotting for ATP6v1c1 from representative cell lines examining relative levels of ATP6v1c1 in C3H10T1/2 (immortalized fibroblast-like), 4T1 (mouse mammary cancer), MCF7, MDA-MB-231, and MDA-MB-435s (human breast cancer) cells. B. Quantification of A (n=3). C. Western blot analysis of the efficacy of various shRNA targeting the human ATP6V1C1 sequence in MDA-MB-435s cells. We used tubulin as a protein loading. Lane C, SHC002 as a control; Lane 1, TRCN0000029564; Lane 2, TRCN0000029565; Lane 3, TRCN0000029566; Lane 4, TRCN0000029567; and Lane 5, TRCN0000029568. D. Quantification of ATP6V1C1 protein expression level (normalized to the tubulin level) in cells treated with lentiviruses expressing different shRNA as indicated (n=3). * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, compared with that of cells treated with SHC002. We selected SHC002 (lane C) as the Scramble shRNA control. We selected TRCN0000029566 (lane 3) and TRCN0000029568 (lane 5) as shRNA-1 and shRNA-2 respectively. E-G. ATP6V1C1 knockdown in MDA-MB-231 inhibited cell proliferation and mTOR pathway activation stimulated by amino acid stimulation. (E) Representative data of anti-BrdU staining of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with different lentiviruses as indicated after 3 hours incubation with BrdU (Red arrows show the BrdU positive cells. Blue arrows show the BrdU negative cells). (F) Quantification of percentage of BrdU positive cells per view. (n=10). (G) Representative data of p-p70S6K, p-AKT, p-ERK1/2 and ATP6V1C1 expression in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with different lentiviruses with or without amino acid stimulation as indicated by Western blotting.
